Question: The following data were obtained in a BET apparatus for adsorption equilibrium of N 2 on silica gel (SG) at 195.8C. Estimate Sg in m
The following data were obtained in a BET apparatus for adsorption equilibrium of N2 on silica gel (SG) at –195.8°C. Estimate Sg in m2/g of silica gel. How does your value compare with that in Table 15.2?
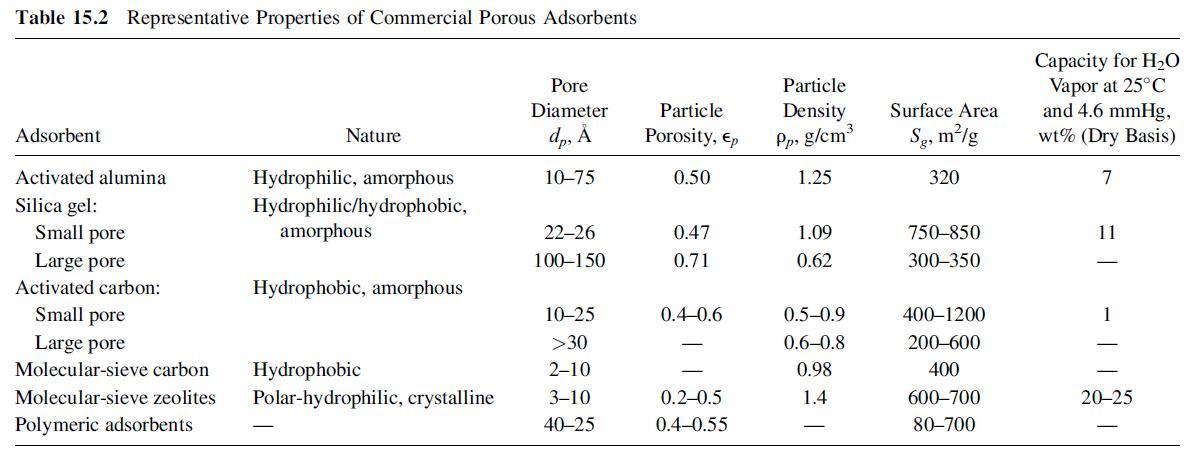

Table 15.2 Representative Properties of Commercial Porous Adsorbents Adsorbent Activated alumina Silica gel: Small pore Large pore Activated carbon: Small pore Large pore Molecular-sieve carbon Molecular-sieve zeolites Polymeric adsorbents Nature Hydrophilic, amorphous Hydrophilic/hydrophobic, amorphous Hydrophobic, amorphous Pore Diameter dp, A 10-75 22-26 100-150 10-25 >30 Hydrophobic 2-10 Polar-hydrophilic, crystalline 3-10 40-25 Particle Porosity, Ep 0.50 0.47 0.71 0.4-0.6 0.2-0.5 0.4-0.55 Particle Density Pp, g/cm 1.25 1.09 0.62 0.5-0.9 0.6-0.8 0.98 1.4 Surface Area Sg, m/g 320 750-850 300-350 400-1200 200-600 400 600-700 80-700 Capacity for HO Vapor at 25C and 4.6 mmHg, wt% (Dry Basis) 7 11 - 118 20-25
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To estimate Sg the specific surface area of silica gel you will n... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


