Question: Consider a system represented by a first-order ordinary differential equation: (a) Show first that for a function f(t) using the definition of the derivative. (b)
Consider a system represented by a first-order ordinary differential equation:
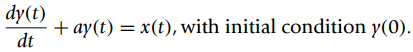
(a) Show first that for a function f(t)
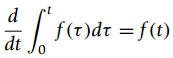
using the definition of the derivative.
(b) Apply the above result to show that the solution of the first-order ordinary differential equation with initial condition y(0) given above is
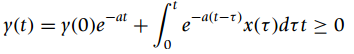
(c) Another way to show the above expression is the solution of the ordinary differential equation is to multiply both sides of the ordinary differential equation by eat
i. show that the left term is d(eat y(t))/dt,
ii. integrate the two terms to obtain the solution.
|dy(t) + ay(t) = x(t), with initial condition y(0). dt dt f(t)dr = f(t) %3D
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (163 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a By the definition of the derivative b yt satisfies the ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


