Bacteria Colonies: Poisson Distribution A pathologist has been studying the frequency of bacterial colonies within the field
Question:
Bacteria Colonies: Poisson Distribution A pathologist has been studying the frequency of bacterial colonies within the field of a microscope using samples of throat cultures from healthy adults.
Long-term history indicates that there is an average of 2.80 bacteria colonies per field. Let r be a random variable that represents the number of bacteria colonies per field. Let O represent the number of observed bacteria colonies per field for throat cultures from healthy adults. A random sample of 100 healthy adults gave the following information.
r 0 1 2 3 4 5 or more O 12 15 29 18 19 7
(a) The pathologist wants to use a Poisson distribution to represent the probability of r, the number of bacteria colonies per field. The Poisson distribution is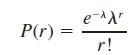
where l 5 2.80 is the average number of bacteria colonies per field. Compute P r ( ) for r 5 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 or more.
(b) Compute the expected number of colonies E 5100P (r ) for r 5 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 or more.
(c) Compute the sample statistic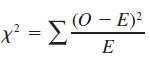
and the degrees of freedom.
(d) Test the statement that the Poisson distribution fits the sample data. Use a 5% level of significance.AppendixLO1
Step by Step Answer:

Understandable Statistics Concepts And Methods
ISBN: 9780357719176
13th Edition
Authors: Charles Henry Brase, Corrinne Pellillo Brase





