A strain gauge is a resistive device that measures the elongation (strain) of a solid material caused
Question:
A strain gauge is a resistive device that measures the elongation (strain) of a solid material caused by applied forces (stress). A typical strain gauge consists of a thin film of conducting material deposited on an insulating substrate. When the gauge is bonded to a member under stress, its resistance changes by
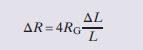
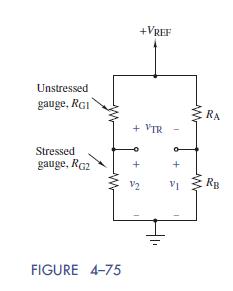
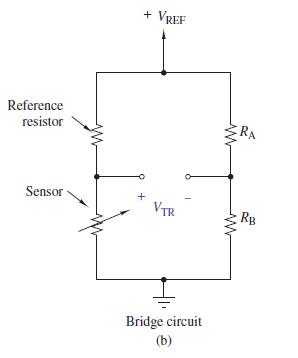
where RG is the resistance of the gauge with no applied stress and ΔL=L is the elongation of the material expressed as a fraction of the unstressed length L. The change in resistance ΔR is only a tenth of an ohm or so, which is far too little to be measured with an ohmmeter. To detect such a small change, the strain gauge is placed in a Wheatstone bridge circuit like the one shown in Figure 4–71(b). The bridge contains fixed resistors RA and RB, two matched strain gauges RG1 [the reference resistor in Figure 4–71(b)] and RG2 [the passive transducer or sensor in Figure 4–71(b)], and a precisely controlled reference voltage VREF. The values of RA and RB are chosen so that the bridge is balanced ðυTR = 0Þ when no stress is applied.When stress is applied, the resistance of the stressed gauge changes to RG2 +ΔR and the bridge is unbalanced ðυTR 6¼ 0Þ. The differential signal ðυTRÞ indicates the strain resulting fromthe applied stress. See Figure 4–75.
Design an OP AMP circuit to translate strains in the range 0
Step by Step Answer:

The Analysis And Design Of Linear Circuits
ISBN: 9781119235385
8th Edition
Authors: Roland E. Thomas, Albert J. Rosa, Gregory J. Toussaint





