The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has a high mutation rate. Many of the mutations that appear are
Question:
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) has a high mutation rate. Many of the mutations that appear are harmful to the virus itself, making it less able to replicate. Are mutations in all genes of the virus equally harmful? Theys et al. (2018) measured the reduction in replication rate of HIV viruses caused by mutations in two different genes, reverse transcriptase (RT) and protease (pro). The accompanying graphs show the frequency distributions of reductions in replication rates for 158 and 397 unique mutations that affect the amino acid sequence of the two proteins. We also show the distributions of the same data after log transformation.
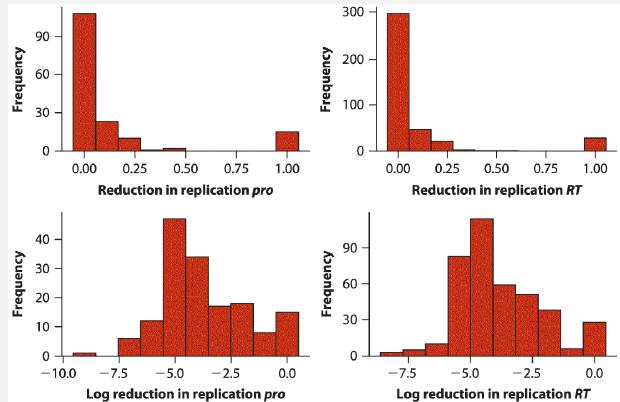
a. What features of the frequency distribution of the data suggest that transformation is necessary? What features suggests that a log transformation is worth trying?
b. Do the distributions of the log-transformed data look like they came from a normal distribution? Comment on the suitability of a t-test for analyzing these results, given the large sample sizes.
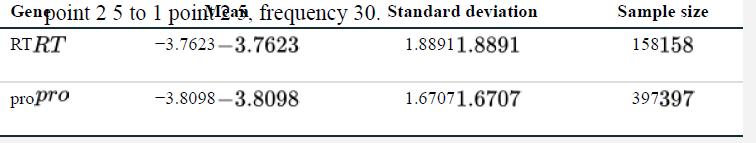
c. Perform a suitable test to compare the means of the reduction in replication rates between RT and pro mutations in HIV.
Step by Step Answer:

The Analysis Of Biological Data
ISBN: 9781319226237
3rd Edition
Authors: Michael C. Whitlock, Dolph Schluter





