The unit of contraction within skeletal muscle cells is called the sarcomere. A sarcomere contracts when the
Question:
The unit of contraction within skeletal muscle cells is called the sarcomere. A sarcomere contracts when the filamentous protein myosin stretches into a high-energy conformation and binds to the filamentous protein actin. When the myosin returns to its low-energy, relaxed conformation, actin is pulled, and the sarcomere contracts. The following steps relate ATP to each step of this process.
1- Myosin binds to actin (ADP is attached).
2- Myosin returns to low-energy conformation (ADP is released).
3- Myosin releases actin (ATP binds).
4- Myosin stretches to high-energy conformation (ATP is hydrolyzed).
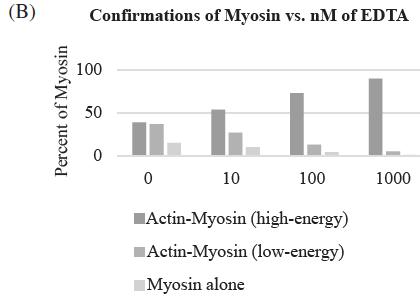
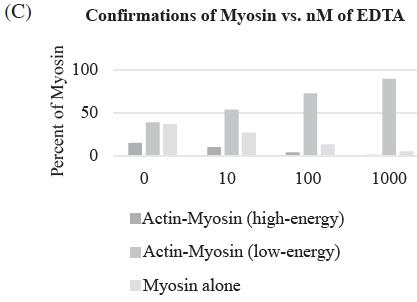
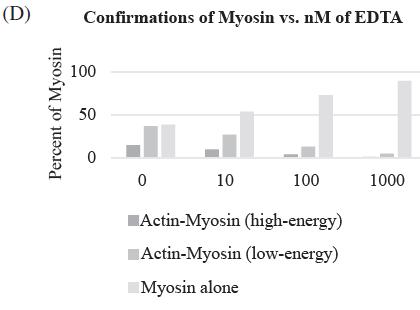
A calcium ion is required for the binding of myosin to actin. If a calcium chelator, such as EDTA, is added to a muscle cell, which of the following graphs shows how it will affect muscle contraction?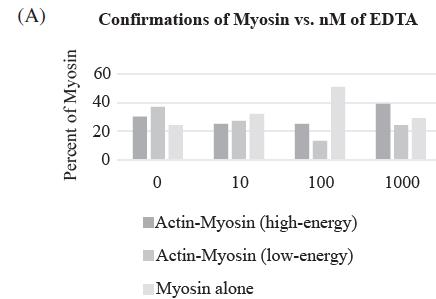
Step by Step Answer:

The Princeton Review AP Biology Premium Prep 2023
ISBN: 9780593450659
2023 Edition
Authors: The Princeton Review





