Question:
A mixture of ideal gases contains 0.5 kmol of CO2, 2 kmol of O2, and 7 kmol of N2 at 700 K. Determine the following quantities:
A. The mole fraction of each constituent in the mixture.
B. The apparent molecular weight of the mixture.
C. The volume of the mixture when the pressure is 600 kPa.
D. The apparent specific heat at constant pressure using a mass basis (cv,mix in kJ/kg·sK) and molar basis (cv,mix in kJ/kg·K).Use specific heat values for each species from Table E.1.
E. Find the heat transfer required to decrease the temperature of the mixture from 900 K to 500 K at constant pressure using the apparent specific heat from part D. Assume that the apparent specific heat remains constant during this process.
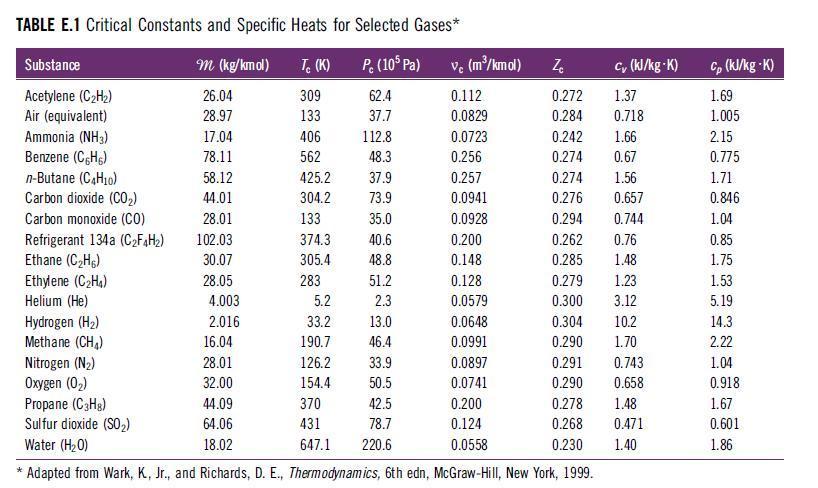
Transcribed Image Text:
TABLE E.1 Critical Constants and Specific Heats for Selected Gases*
P. (105 Pa)
62.4
37.7
Substance
Acetylene (C₂H₂)
Air (equivalent)
Ammonia (NH3)
Benzene (CH₂)
n-Butane (C4H10)
Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Refrigerant 134a (C₂F4H₂)
Ethane (C₂H)
Ethylene (C₂H₁)
Helium (He)
m (kg/kmol)
26.04
28.97
17.04
78.11
58.12
44.01
28.01
102.03
30.07
28.05
4.003
2.016
Tc (K)
309
133
406
562
16.04
28.01
32.00
425.2
304.2
133
374.3
305.4
283
5.2
33.2
190.7
126.2
154.4
370
431
647.1
112.8
48.3
37.9
73.9
35.0
40.6
48.8
51.2
2.3
13.0
46.4
33.9
50.5
42.5
78.7
220.6
vc (m³/kmol)
0.112
0.0829
0.0723
0.256
0.257
0.0941
0.0928
0.200
0.148
0.128
0.0579
0.0648
0.0991
0.0897
0.0741
Ze
cy (kJ/kg-K)
0.272
1.37
0.284 0.718
0.242
1.66
0.274 0.67
1.56
0.657
0.744
0.76
1.48
0.274
0.276
0.294
0.262
0.285
0.279
1.23
0.300 3.12
10.2
1.70
Hydrogen (H₂)
Methane (CH₂)
Nitrogen (N₂)
Oxygen (0₂)
Propane (C₂H₂)
44.09
0.200
Sulfur dioxide (SO₂)
64.06
0.124
Water (H₂O)
18.02
0.0558
* Adapted from Wark, K, Jr., and Richards, D. E., Thermodynamics, 6th edn, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1999.
0.304
0.290
0.291 0.743
0.290 0.658
0.278
1.48
0.268 0.471
0.230
1.40
Cp (kJ/kg-K)
1.69
1.005
2.15
0.775
1.71
0.846
1.04
0.85
1.75
1.53
5.19
14.3
2.22
1.04
0.918
1.67
0.601
1.86







