Question: A simple pistoncylinder engine operates using a sequence of four processes: 1-2 Compression at constant temperature, maintained by cooling.2-3 Heating at constant volume (by flames).3-4
A simple piston–cylinder engine operates using a sequence of four processes:
1-2 Compression at constant temperature, maintained by cooling.2-3 Heating at constant volume (by flames).3-4 Expansion at constant temperature, maintained by heating (by flames).4-1 Cooling at constant volume back to the initial state (1).onUsing the ideal gas property information in (and following the format of) the Detailed heat pump cycle analysis example of Section 2.8, derive expressions for the energy transfer as work and heat for each process.
Section 2.8
Consider the compression of gas in a cylinder, for example in an air compressor or during the compression stroke in an internal combustion engine (Figure 2.5).
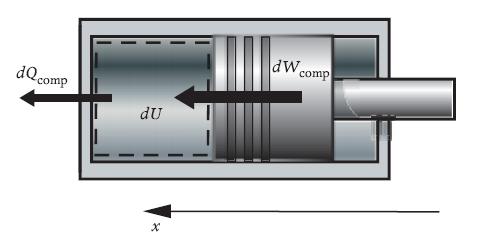
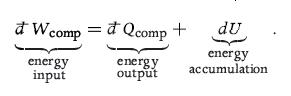
We use our special d− symbol since d−Wcomp and d−Qcomp represent infinitesimal amounts of energy transfer. If we integrate (2.8a) over the entire compression process, we get the energy balance for the entire compression process,
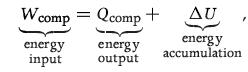
Express the efficiency of the cycle, η ≡ Wnet output/Qinputfrom flames , as a function of the compression ratio rV = V1/V2 and the temperature ratio rT = T3/T1. Plot the efficiency over the rV range 1–20 for rT = 2 and 5, for γ = 7/5. Does this look like a promising engine cycle?
dQc comp du MP comp
Step by Step Solution
3.34 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
We can use the ideal gas law PVnRT to derive expressions for the energy transfer as work and heat for each process in the given pistoncylinder engine 12 Compression at constant temperature maintained ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


