The magnetocaloric effect is defined by the temperature variation observed in a material under adiabatic conditions when
Question:
The magnetocaloric effect is defined by the temperature variation observed in a material under adiabatic conditions when the applied magnetic induction field B varies. The effect becomes particularly large when the material undergoes a phase transition due to the magnetic induction field variation. An application of this effect was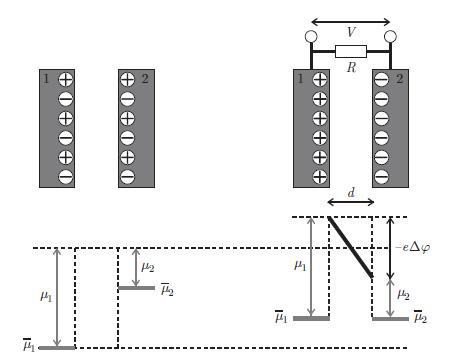 A parallel plate capacitor is made of metals 1 and 2 which have electrochemical potentials ¯μ1 and ¯μ2 and chemical potentials μ1 and μ2. On the left, the plates are not connected and the electrochemical potentials are not equal. On the right, when conduction electrons of charge e (sign included) are allowed to flow, the electrochemical potentials are equal. If the spacing d varies over time, electric charges flow through the resistance R and a voltage V can be measured. considered for space exploration [135]. The applied magnetic induction field may be produced by permanent magnets [136]. Show that the infinitesimal temperature variation dT during an adiabatic process characterised by an infinitesimal magnetic induction field variation dB at constant pressure is given by,
A parallel plate capacitor is made of metals 1 and 2 which have electrochemical potentials ¯μ1 and ¯μ2 and chemical potentials μ1 and μ2. On the left, the plates are not connected and the electrochemical potentials are not equal. On the right, when conduction electrons of charge e (sign included) are allowed to flow, the electrochemical potentials are equal. If the spacing d varies over time, electric charges flow through the resistance R and a voltage V can be measured. considered for space exploration [135]. The applied magnetic induction field may be produced by permanent magnets [136]. Show that the infinitesimal temperature variation dT during an adiabatic process characterised by an infinitesimal magnetic induction field variation dB at constant pressure is given by,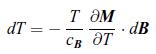 where cB is the specific heat per unit volume at constant magnetic induction field B.
where cB is the specific heat per unit volume at constant magnetic induction field B.
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9781108426091
1st Edition
Authors: Jean-Philippe Ansermet, Sylvain D. Brechet





