Question: Another researcher selected two random samples from one population. This population has a mean of 63 (μ = 63). It turned out that each sample
Another researcher selected two random samples from one population. This population has a mean of 63 (μ = 63). It turned out that each sample had the same mean (M = 60) and standard deviation (s = 5). The only way the two samples differed was in terms of size: one, C, was smaller (N = 10) and one, D, was larger (N = 50). The researcher went on to conduct a single-sample t test for each sample. Based on the information provided below, how does sample size affect the results of a single-sample t test?
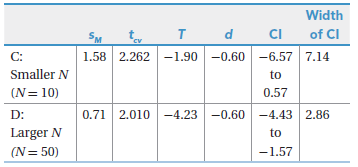
Width CI of CI SM 2.262 -1.90 -0.60 -6.577.14 1.58 C: Smaller N to (N= 10) 0.57 0.71 2.010 -4.23 -0.60 -4.43 2.86 D: Larger N to (N= 50) -1.57
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (177 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The larger the sample size a The smaller the standard error of the mean b Th... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


