The amount of a uniformly distributed radioactive contaminant contained in a close reactor is measured by its
Question:
The amount of a uniformly distributed radioactive contaminant contained in a close reactor is measured by its concentration c (Becquerel/liter or Bq/L). The contaminant decreases at a decay rate proportional to its concentration-that is Decay rate = -kc where k is a constant with units of day?1. Therefore, according to Eq. (1.13), a mass balance for the reactor can be written as
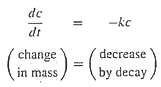
(a) Use Euler?s method to solve this equation from t = 0 to 1 d with k = 0.2d?1. Employ a step size of ?t = 0.1. The concentration at t = 0 is 10 Bq/L.
(b) Plot the solution on a semilog graph (i.e., in c versus t) and determine the slope. Interpret your results.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Numerical Methods For Engineers
ISBN: 9780071244299
5th Edition
Authors: Steven C. Chapra, Raymond P. Canale
Question Posted:





