A plastic tube of 7.6-cm ID and 1.27 cm wall thickness having a thermal conductivity of 1.7
Question:
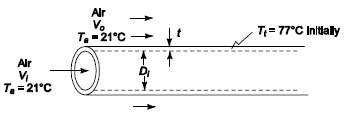
A plastic tube of 7.6-cm ID and 1.27 cm wall thickness having a thermal conductivity of 1.7 W/(m K), a density of 2400 kg/m3, and a specific heat of 1675 J/(kg K) is cooled from an initial temperature of 77?C by passing air at 20?C inside and outside the tube parallel to its axis. The velocities of the two air streams are such that the coefficients of heat transfer are the same on the interior and exterior surfaces. Measurements show that at the end of 50 min, the temperature difference between the tube surfaces and the air is 10 percent of the initial temperature difference. It is proposed to cool a tube of a similar material having an inside diameter of 15 cm and a wall thickness of 2.5 cm from the same initial temperature, also using air at 20?C and feeding to the inside of the tube the same number of kilograms of air per hour that was used in the first experiment. The airflow rate over the exterior surfaces will be adjusted to give the same heat transfer coefficient on the outside as on the inside of the tube. It may be assumed that the airflow rate is so high that the temperature rise along the axis of the tube may be neglected. Using the experience gained initially with the 4.5-cm tube, estimate how long it will take to cool the surface of the larger tube to 27?C under the conditions described. Indicate all assumptions and approximations in your solution.GIVENAir flow inside and outside a plastic tubeCase 1Tube 1 inside diameter (D1i) = 7.6 cm = 0.076 mTube 1 wall thickness (S1) = 1.27 cm = 0.0127 mPlastic propertiesThermal conductivity (kp) = 1.7 W/(m K)Density (ρ) = 2400 kg/m3Specific heat (c) = 1675 J/(kg K)Tube initial temperature (Tti) = 77?CAir temperature (Ta) = 20?CAfter 10 min: (Tt ?? Ta) = 10% of initial (Tt ?? Ta)Case 2Tube 2 inside diameter (D2i) = 15 cm = 0.15 mTube 2 wall thickness (S2) = 2.5 cm = 0.025 mSame initial temperature and air temperature as Case 1Same interior air flow rate as Case 1Air velocities are such that heat transfer coefficients inside and outside are equalASSUMPTIONSTemperature rise along the tube is negligibleTube may be treated as a lumped capacitance (This will bechecked)
Step by Step Answer:

Principles of heat transfer
ISBN: 978-0495667704
7th Edition
Authors: Frank Kreith, Raj M. Manglik, Mark S. Bohn





