Question: In Examples 15.11 and 15.13, benzene is adsorbed from air at 70?F in a 6-ft-high bed of silica gel and then stripped with air at
In Examples 15.11 and 15.13, benzene is adsorbed from air at 70?F in a 6-ft-high bed of silica gel and then stripped with air at 145?F. If the bed height is changed to 30 ft, the following data are obtained for breakthrough at 641 minutes for the adsorption step:
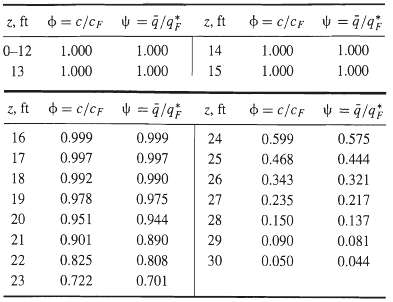
If the bed is regenerated isothermally with pure air at 1 atm and 145oF, and the desorption of benzene during the heatup period is neglected, determine the loading, q, profile at a time sufficient to remove 90% of the benzene from the bed if an interstitial pure air velocity of 98.5 ft/min is used. Values of k and K at 145?F are given in Example 15.13.
z, ft $ = c/CF V = 7/9 V = 7/a; o = c/CF 0-12 1.000 1.000 14 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 13 15 = 4/q; O = c/CF z, ft = c/CF 2, ft V = q/q 0.999 16 0.999 24 0.575 0.599 0.997 17 0.997 25 0.468 0.444 18 0.992 0.990 26 0.343 0.321 19 0.978 0.975 27 0.235 0.217 20 0.951 0.944 28 0.150 0.137 21 0.901 0.890 29 0.090 0.081 22 0.825 0.808 30 0.050 0.044 23 0.722 0.701
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (173 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
First compute the initial amount of benzene adsorbed in the bed However the breakthrough at 641 minutes corresponds to cc F 005 and not at 0 Therefore ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
37-E-C-E-S-P (542).docx
120 KBs Word File


