Question: Low-density phenomena in compressible tube flow2,3 (Fig. 2B.9). As the pressure is decreased in the system studied in Example 2.3-2, deviations from Eqs. 2.3-28 and
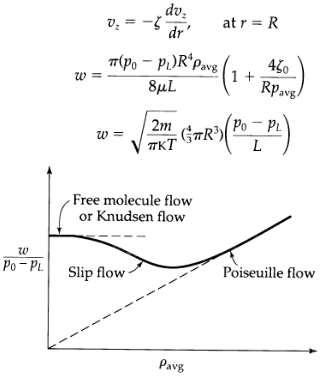
Low-density phenomena in compressible tube flow2,3 (Fig. 2B.9). As the pressure is decreased in the system studied in Example 2.3-2, deviations from Eqs. 2.3-28 and 2.3-29 arise. The gas behaves as if it slips at the tube wall. It is conventional2 to replace the customary "no-slip" boundary condition that vz = 0 at the tube wall by in which ? is the slip coefficient. Repeat the derivation in Example 2.3-2 using Eq. 2B.9-1 as the boundary condition. Also make use of the experimental fact that the slip coefficient varies inversely with the pressure ? = ?0/p, in which ?0 is a constant. Show that the mass rate of flow is in which Pavg = ½(p0 + p1) When the pressure is decreased further, a flow regime is reached in which the mean free path of the gas molecules is large with respect to the tube radius (Knudsen flow). In that regime3 in which m is the molecular mass and K is the Boltzmann constant. In the derivation of this result it is assumed that all collisions of the molecules with the solid surfaces are diffuse and not specular, the results in Eqs. 2.3-29, 2B.9-2, and 2B.9-3 are summarized in Fig. 2B.9.
W Po-PL W v = -5 dv dr _H/P: - PUR Pas (1 +26) (Po Pavg 450 8L avg w= w - /2m (GwR (P = P) = GR) TKT L Free molecule flow or Knudsen flow Slip flow at r = R Pavg Poiseuille flow
Step by Step Solution
3.24 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Lowdensity phenomena in compressible tube flow When we replace noslip boundary condition of Eq 2317 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
6-E-C-E-T-P (28).docx
120 KBs Word File


