On January 1, 2010, Parker, Inc., a U.S.-based firm, acquired 100 percent of Suffolk PLC located in
Question:
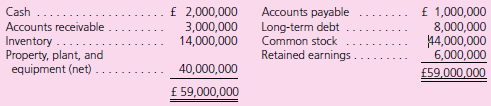
Suffolk€™s 2010 income was recorded at £2,000,000. It declared and paid no dividends in 2010. On December 31, 2011, two years after the date of acquisition, Suffolk submitted the following trial balance to Parker for consolidation:
Cash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . £ 1,500,000
Accounts Receivable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5,200,000
Inventory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18,000,000
Property, Plant, and Equipment (net) . . . . . . . . 36,000,000
Accounts Payable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .(1,450,000)
Long-Term Debt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .(5,000,000)
Common Stock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (44,000,000)
Retained Earnings (1/1/11) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (8,000,000)
Sales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . (28,000,000)
Cost of Goods Sold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16,000,000
Depreciation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2,000,000
Other Expenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6,000,000
Dividends Paid (1/30/11) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1,750,000
€“0€“
Other than paying dividends, no intra-entity transactions occurred between the two companies. Relevant exchange rates for the British pound follow:
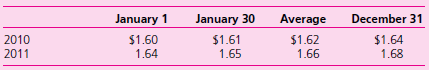
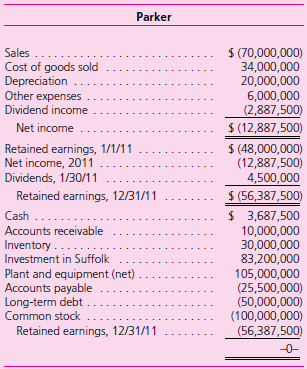
The December 31, 2011, financial statements (before consolidation with Suffolk) follow. Dividend income is the U.S. dollar amount of dividends received from Suffolk translated at the $1.65/£ exchange rate at January 30, 2011. The amounts listed for dividend income and all affected accounts (i.e., net income, December 31 retained earnings, and cash) reflect the $1.65/£ exchange rate at January 30, 2011. Credit balances are in parentheses.
Parker's chief financial officer (CFO) wishes to determine the effect that a change in the value of the British pound would have on consolidated net income and consolidated stockholders' equity. To help assess the foreign currency exposure associated with the investment in Suffolk, the CFO requests assistance in comparing consolidated results under actual exchange rate fluctuations with results that would have occurred had the dollar value of the pound remained constant or declined during the first two years of Parker's ownership.
Required
Use an electronic spreadsheet to complete the following four parts:
Part I. Given the relevant exchange rates presented,
a. Translate Suffolk's December 31, 2011, trial balance from British pounds to U.S. dollars. The British pound is Suffolk's functional currency.
b. Prepare a schedule that details the change in Suffolk's cumulative translation adjustment (beginning net assets, income, dividends, etc.) for 2010 and 2011.
c. Prepare the December 31, 2011, consolidation worksheet for Parker and Suffolk.
d. Prepare the 2011 consolidated income statement and the December 31, 2011, consolidated balance sheet. Note:Worksheets should possess the following qualities:
€¢ Each spreadsheet should be programmed so that all relevant amounts adjust appropriately when different values of exchange rates (subsequent to January 1, 2010) are entered into it.
€¢ Be sure to program Parker's dividend income, cash, and retained earnings to reflect the dollar value of alternative January 30, 2011, exchange rates.
Part II. Repeat tasks (a), (b), (c), and (d) from Part I to determine consolidated net income and consolidated stockholders' equity if the exchange rate had remained at $1.60/£ over the period 2010 to 2011.
Part III. Repeat tasks (a), (b), (c), and (d) from Part I to determine consolidated net income and consolidated stockholders€™ equity if the following exchange rates had existed:
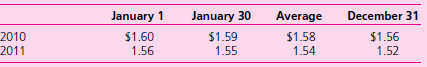
Part IV. Prepare a report that provides Parker€™s CFO the risk assessments requested. Focus on profitability, cash flow, and the debt-to-equity ratio.
Please visit the text Web site for the online CPA Simulation
Situation: Texas Corporation, located in San Antonio, has transactions both in the United States and in Mexico although the U.S. dollar is its functional currency. In addition, Texas has a wholly owned subsidiary (Mexico, Inc.) located in Mexico. Consolidated financial statements are being prepared for Year 1. The currency exchange rates are as follows for the current year (Year 1):
€¢ January 1, Year 1: 1 peso equals $0.088.
€¢ Average for Year 1: 1 peso equals $0.090.
€¢ November 1, Year 1: 1 peso equals $0.092.
€¢ December 1, Year 1: 1 peso equals $0.094.
€¢ December 31, Year 1: 1 peso equals $0.095.
€¢ January 31, Year 2: 1 peso equals $0.098.
Topics to be covered in simulation:
€¢ Remeasurement process.
€¢ Translation process.
€¢ Foreign currency balances€”impact on net income.
€¢ Foreign currency balances€”impact on comprehensive income.
€¢ Translation adjustment.
€¢ Functional currency.
€¢ Forward exchange contracts as a cash flow hedge.
€¢ Forward exchange contracts as a fair value hedge.
Financial StatementsFinancial statements are the standardized formats to present the financial information related to a business or an organization for its users. Financial statements contain the historical information as well as current period’s financial... Consolidated Income Statement
When talking about the group financial statements the consolidated financial statements include Consolidated Income Statement that a parent must prepare among other sets of consolidated financial statements. Consolidated Income statement that is... Dividend
A dividend is a distribution of a portion of company’s earnings, decided and managed by the company’s board of directors, and paid to the shareholders. Dividends are given on the shares. It is a token reward paid to the shareholders for their... Exchange Rate
The value of one currency for the purpose of conversion to another. Exchange Rate means on any day, for purposes of determining the Dollar Equivalent of any currency other than Dollars, the rate at which such currency may be exchanged into Dollars...
Step by Step Answer:

Advanced Accounting
ISBN: 978-0077431808
10th edition
Authors: Joe Hoyle, Thomas Schaefer, Timothy Doupnik





