Question: A radiant heater, which is used for surface treatment processes, consists of a long cylindrical heating element of diameter D 1 = 0.005 m and
A radiant heater, which is used for surface treatment processes, consists of a long cylindrical heating element of diameter D1 = 0.005 m and emissivity ?1 = 0.80. The heater is partially enveloped by a long, thin parabolic reflector whose inner and outer surface emissivities are ?2i = 0.10 and ?20 = 0.80, respectively. Inner and outer surface areas per unit length of the reflector are each A2i = A2o = 0.20 m, and the average convection coefficient for the combined inner and outer surfaces is h 2(i, o) = 2 W/m2 ? K. The system may be assumed to be in an infinite, quiescent medium of atmospheric air at T? = 300 K and to be exposed to large surroundings at Tsur = 300 K.
(a) Sketch the appropriate radiation circuit, and write expressions for each of the network resistances.
(b) If, under steady-state conditions, electrical power is dissipated in the heater at P1 = 1500 W/m and the heater surface temperature is T1 = 1200 K, what is the net rate at which radiant energy is transferred from the heater?
(c) What is the net rate at which radiant energy is transferred from the heater to the surroundings?
(d) What is the temperature, T2, of the reflector?
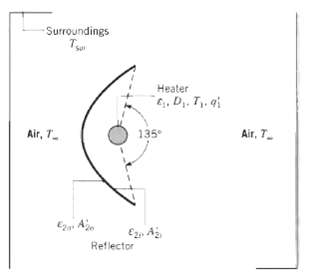
Surroundings Heater e, D,. T. q Air, T. 135 Air, T Ez A Reflector
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Temperature power dissipation and emissivity of a cylindrical heat source Surface emissivities of a parabolic reflector Temperature of air and s... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (1339).docx
120 KBs Word File


