Question: A random process X (t) is defined by X (t) = A cos (2? f c t), where A is a Gaussian-distributed random variable of
A random process X (t) is defined by X (t) = A cos (2? f c t), where A is a Gaussian-distributed random variable of zero means variance ?2A. This random process is applied to an ideal integrator, producing the output
(a) Determine the probability density function of the output Y (t) at a particular time tk.
(b) Determine whether or not Y (t) is stationary.
(c) Determine whether or not Y (t) is ergodic.
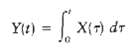
= X(-) dr Y(t)
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a The integrator output at time t is Yt XT dT 0 A cos2ft dr 0 Therefore A E Y t sin2 ft sin2nf t 2... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
19-E-T-E-C-S (3).docx
120 KBs Word File


