A solar collector consists of a long duct through which air is blown; its cross section forms
Question:
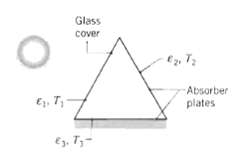
A solar collector consists of a long duct through which air is blown; its cross section forms an equilateral triangle 1 m on a side. One side consists of a glass cover of emissivity ?1 = 0.9, while the other two sides are absorber plates with ?2 = ?3 = 1.0. During operation the surface temperatures are known to be T1 = 25?C, T2 = 60?C, and T3?= 70?C. What is the net rate at which radiation is transferred to the cover due to exchange with the absorber plates?
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
ISBN: 978-0471457282
6th Edition
Authors: Incropera, Dewitt, Bergman, Lavine
Question Posted:





