The information is the same as in P10.13 except that on 1 October 20x1, the management of
Question:
The information is the same as in P10.13 except that on 1 October 20x1, the management of Eastern Company acquired 50 options contracts that gave the holder the right but not the obligation to sell 100,000 one-ounce silver coins per contract at a price of $3.30 per coin. The option contracts expired on 31 March 20x2. The premiums on the option are as follows:

The management of Eastern Company designated the options contracts as a hedge of the fair value of the inventory.
The time value of the options was excluded from the hedging relationship. The entire inventory was sold off on 31 March 20x2 at $3.10 per coin.
Required
1. Show the journal entries for the hedging instrument and the hedged item from 1 October 20x1 to 31 March 20x2.
2. Compare the profit on the sale of the inventory with and without hedging.
Data from P10.13
Eastern Company had inventory of 5,000,000 one-ounce silver coins, which were carried at a cost of $15 million
(current market value is $16.5 million). The selling price of the silver coins was largely determined by the spot price of silver, which accounted for the bulk of the manufacturing costs. In recent months, the price of silver had risen substantially due to disruption in supply as a result of strikes in Australia, which is the main producer of silver. The management of Eastern Company was concerned about a potential fall in the price of silver when the supply shortage eases. To hedge against this risk, the management of Eastern Company sold silver futures contracts with a total notional quantity of 5 million ounces at $3.21 per ounce on 1 October 20x1. The contract matured on 31 March 20x2. The commodity exchange required a margin deposit of $0.03 per ounce for the futures contract. The level of margin deposit had to be maintained at all times.
The management of Eastern Company had designated the futures contracts as a cash flow hedge of the anticipated sale of silver coins. Past experience had proven that there was a very high correlation between the spot price of silver and the selling price of silver coins. Therefore, the management expected that the futures contracts were an effective hedge of the anticipated sale and that the other conditions for hedge accounting were met. For the purpose of assessing hedge effectiveness, the entire change in the fair value of the futures contract was compared with the change in the expected cash flows. The spot prices of silver coins and the prices of silver futures contracts for 31 March 20x2 delivery are as follows:
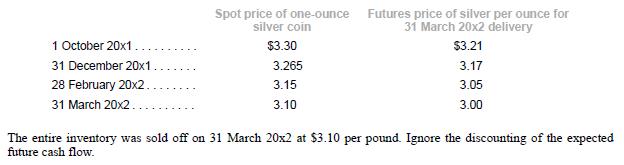
Step by Step Answer:

Advanced Financial Accounting An IFRS Standards Approach
ISBN: 9781285428765
4th Edition
Authors: Pearl Tan, Chu Yeong Lim, Ee Wen Kuah





