Boron trifluoride, B F 3 B F 3 , is a planar molecule with F B
Question:
Boron trifluoride, , is a planar molecule with bond angles of . It has the same symmetry operations as the mass and spring system in Problems 8 and 9, hence has the same character table. Its nontrivial normal modes are basis functions for the irreducible representations .
(a) Which of the modes are IR active?
(b) Which of the modes are Raman active?
(c) Which mode is Raman active but not IR active?
Data from Problem 8
Consider a planar system of three identical masses and three identical springs. At equilibrium each mass is at the apex of an equilateral triangle. A spring links each pair of masses.
How many displacement coordinates are there?
How many normal modes are there?
One of the normal modes is a basis function for the identity irreducible representation. Sketch this normal mode.
Data from Problem 9
Consider a planar system of three identical masses and three identical springs. At equilibrium each mass is at the apex of an equilateral triangle. A spring links each pair of masses.
Here is its character table (inversions omitted).
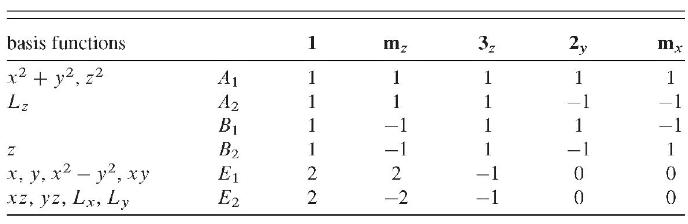
Use coordinate displacements as the basis for a reducible representation. In this representation what are the characters of each of the symmetry operations listed in the table?
Step by Step Answer:

An Introduction To Groups And Their Matrices For Science Students
ISBN: 9781108831086
1st Edition
Authors: Robert Kolenkow