Question: 1 Monte Carlo localization is biased for any finite sample sizei.e., the expected value of the location computed by the algorithm differs from the true
1 Monte Carlo localization is biased for any finite sample size—i.e., the expected value of the location computed by the algorithm differs from the true expected value—because of the way particle filtering works. In this question, you are asked to quantify this bias.
To simplify, consider a world with four possible robot locations: X = {x1, x2, x3, x4}.
Initially, we draw N ≥ 1 samples uniformly from among those locations. As usual, it is perfectly acceptable if more than one sample is generated for any of the locations X. Let Z be a Boolean sensor variable characterized by the following conditional probabilities:
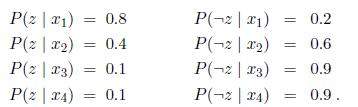
= 0.4 P(-2 | 21) P(-2|22) = 0.2 0.6 P(2 x1) = 0.8 P(2 x2) P(2 3) = 0.1 P(2x4) = 0.1 P(-2 | 3) = 0.9 P(-2|24) 0.9.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


