Sampling and materiality are both related to audit risk. Discuss. The magnitude of an omission or misstatement
Question:
Sampling and materiality are both related to audit risk. Discuss.
The magnitude of an omission or misstatement that, individually or in the aggregate, could reasonably be expected to influence the economic decisions of the users of the financial statements. Materiality provides a basis for determining the nature and extent of our audit procedures.
We determined materiality for the Group to be £34 million, which is 5.1 per cent of profit before tax excluding the items described below. We believe that this materiality basis provides us with the best assessment of the requirements of the users of the financial statements. This is consistent with the approach taken in the prior period.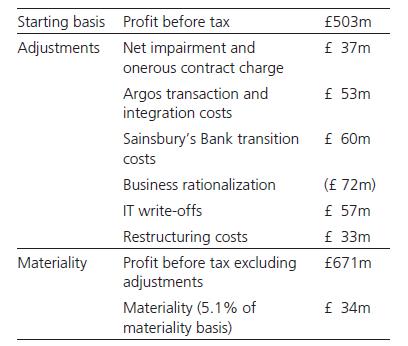
Performance materiality
The application of materiality at the individual account or balance level. It is set at an amount to reduce to an appropriately low level the probability that the aggregate of uncorrected and undetected misstatements exceeds materiality.
On the basis of our risk assessments, together with our assessment of the Group’s overall control environment, our judgement was that performance materiality was approximately 75 per cent (2015/16: 50 per cent) of our planning materiality, namely £25 million (2015/16: £15 million). The reason for the change is that we have assessed the risk of material misstatement to be lower now this is no longer our first audit.
Audit work at component locations for the purpose of obtaining audit coverage over significant financial statement accounts is undertaken based on a percentage of total performance materiality.
The performance materiality set for each component is based on the relative scale and risk of the component to the Group as a whole and our assessment of the risk of misstatement at that component. In the current period, the range of performance materiality allocated to components was £5 million to £19 million (2015/16: £3 million to £11 million).
Reporting threshold
An amount below which identified misstatements are considered as being clearly trivial.
We agreed with the Audit Committee that we would report to them all uncorrected audit differences in excess of £1.7 million (2015/16: £1.5 million), which is set at 5 per cent of planning materiality, as well as differences below that threshold that, in our view, warranted reporting on qualitative grounds.
We evaluate any uncorrected misstatements against both the quantitative measures of materiality discussed above and in light of other relevant qualitative considerations in forming our opinion.
Required:
(a) Discuss the extent to which you believe the above information may be useful to investors and highlight any aspects of the disclosures that are particularly noteworthy.
(b) In addition to the above disclosures can you identify any further information relating to materiality investors might find useful.
Step by Step Answer:

The Audit Process Principles Practice And Cases
ISBN: 9781473760189
7th Edition
Authors: Iain Gray, Louise Crawford, Stuart Manson





