Find the necessary quantities if the given changes are made in the indicated examples of this section.
Question:
Find the necessary quantities if the given changes are made in the indicated examples of this section.
In Example 3, find the resultant velocity if the wind is from the northwest, rather than southeast.
Data from Example 3
An airplane headed due east is in a wind blowing from the southeast. What is the resultant velocity of the plane with respect to the ground if the velocity of the plane with respect to the air is 600̅ km/h and that of the wind is 100̅ km/h? See Fig. 9.34.

If A is the plane’s air vector (air speed and directional heading) and W is the wind vector (wind speed and wind direction), the calculations below can be used to find the magnitude and direction of the resultant ground vector R (ground speed and ground course).

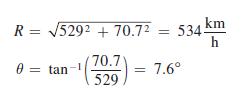
Therefore, the plane is traveling 534 km/h with respect to the ground and is flying on a ground course of 7.6° north of east. From this, we observe that a plane does not necessarily head in the direction of its destination.
Step by Step Answer:

Basic Technical Mathematics
ISBN: 9780137529896
12th Edition
Authors: Allyn J. Washington, Richard Evans





