Make the given changes in the indicated examples of this section, and then solve the resulting problems.
Question:
Make the given changes in the indicated examples of this section, and then solve the resulting problems.
In Example 2, change A(−3,−2) to A(0,−2) and then find the fourth vertex.
Data from Example 2
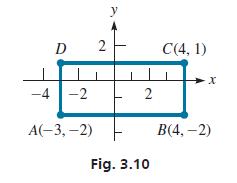
Three vertices of the rectangle in Fig. 3.10 are A(−3,−2), B(4,−2), and C(4, 1). What is the fourth vertex?
We use the fact that opposite sides of a rectangle are equal and parallel to find the solution. Because both vertices of the base AB of the rectangle have a y-coordinate of −2, the base is parallel to the x-axis. Therefore, the top of the rectangle must also be parallel to the x-axis. Thus, the vertices of the top must both have a y-coordinate of 1, because one of them has a y-coordinate of 1. In the same way, the x-coordinates of the left side must both be −3. Therefore, the fourth vertex is D(−3, 1).
Step by Step Answer:

Basic Technical Mathematics
ISBN: 9780137529896
12th Edition
Authors: Allyn J. Washington, Richard Evans





