Design of Experiments You would like to conduct a study to determine the effectiveness of seat belts
Question:
Design of Experiments You would like to conduct a study to determine the effectiveness of seat belts in saving lives in car crashes.
a. What would be wrong with randomly selecting 2000 drivers, then randomly assigning half of them to a group that uses seat belts and another group that does not wear seat belts?
b. If 2000 drivers are randomly selected and separated into two groups according to whether they use seat belts, what is a practical obstacle in conducting a prospective study of the effectiveness of seat belts in car crashes?
1.Birth Rate The birth rate in China is 12.3 per 1000. What exactly does that mean?
2.Rates Exercise 1 describes the birth rate in China as 12.3 per 1000. Another way to describe the birth rate is to give the rate as a proportion or probability of 0.0123. What advantage does the rate of “12.3 per 1000” have over the rate expressed as 0.0123?
3.Expected Births Given that China has a birth rate of 12.3 per 1000 and a population of 1,360,762,587, about how many births are expected in a year?
4.Incidence and Prevalence What is the difference between a disease incidence rate and a disease prevalence rate?
5.Find the neonatal mortality rate.
Finding Rates. In Exercises 5−12, use the data in the accompanying table (based on data for a recent year from various sources, including the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Institutes of Health) to find the indicated rates. Round results to one decimal place, and use a multiplying factor of k 1000 unless indicated otherwise.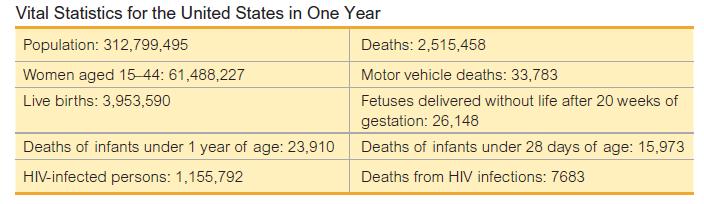 6.Find the fetal mortality rate.
6.Find the fetal mortality rate.
Finding Rates. In Exercises 5−12, use the data in the accompanying table (based on data for a recent year from various sources, including the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Institutes of Health) to find the indicated rates. Round results to one decimal place, and use a multiplying factor of k 1000 unless indicated otherwise.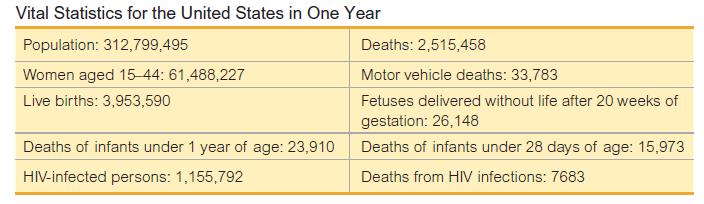 7.Find the perinatal mortality rate.
7.Find the perinatal mortality rate.
Finding Rates. In Exercises 5−12, use the data in the accompanying table (based on data for a recent year from various sources, including the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Institutes of Health) to find the indicated rates. Round results to one decimal place, and use a multiplying factor of k 1000 unless indicated otherwise.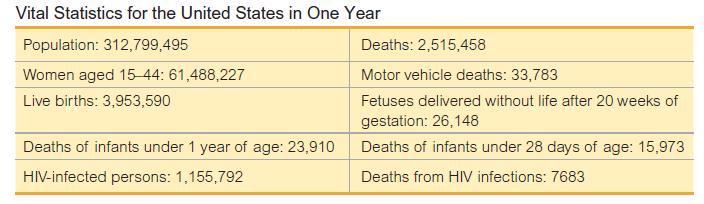 8.Find the crude birth rate.
8.Find the crude birth rate.
Finding Rates. In Exercises 5−12, use the data in the accompanying table (based on data for a recent year from various sources, including the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Institutes of Health) to find the indicated rates. Round results to one decimal place, and use a multiplying factor of k 1000 unless indicated otherwise.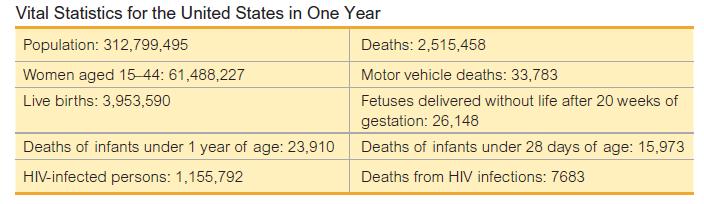 9.Find the general fertility rate.
9.Find the general fertility rate.
Finding Rates. In Exercises 5−12, use the data in the accompanying table (based on data for a recent year from various sources, including the U.S. Census Bureau and the National Institutes of Health) to find the indicated rates. Round results to one decimal place, and use a multiplying factor of k 1000 unless indicated otherwise.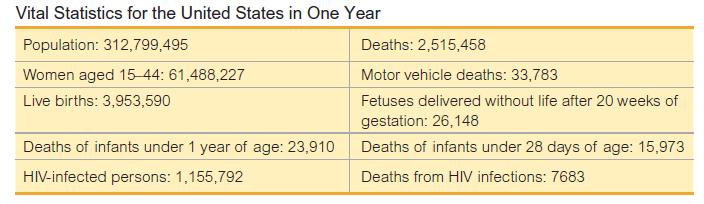
Step by Step Answer:

Biostatistics For The Biological And Health Sciences
ISBN: 9780134039015
2nd Edition
Authors: Marc Triola, Mario Triola, Jason Roy






