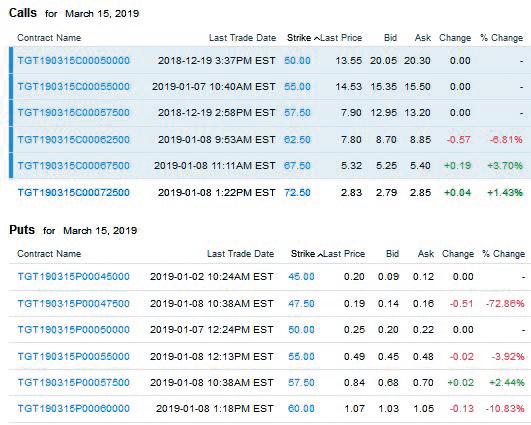
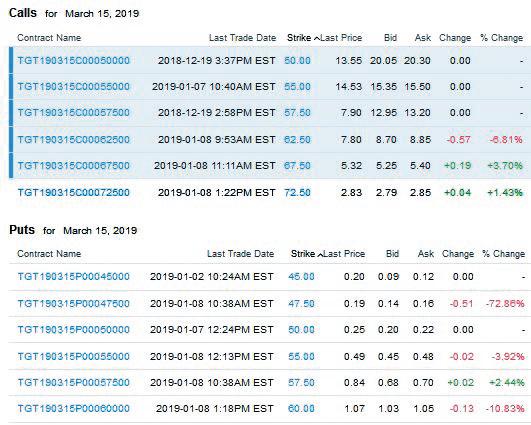
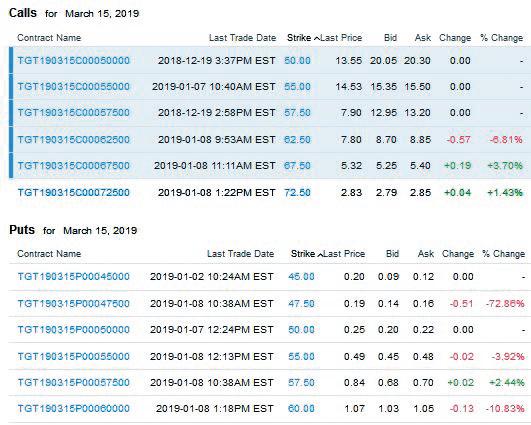
Fundamentals Of Investments Valuation And Management 9th Edition Bradford Jordan, Thomas Miller, Steve Dolvin - Solutions
Discover a comprehensive resource for mastering the "Fundamentals Of Investments Valuation And Management 9th Edition" by Bradford Jordan, Thomas Miller, and Steve Dolvin. Access online answers key and solutions PDF that offer in-depth, step-by-step answers to solved problems and questions from the textbook. Enhance your understanding with our solution manual and chapter solutions, available for free download. Whether you're looking for a test bank or an instructor manual, our collection provides detailed questions and answers to guide your learning journey. Elevate your proficiency with this essential educational tool.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()