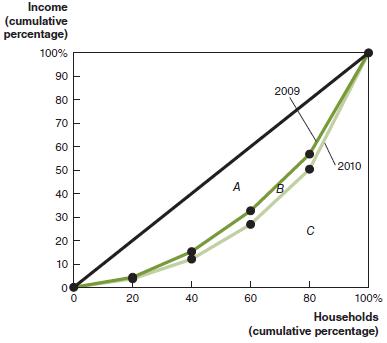
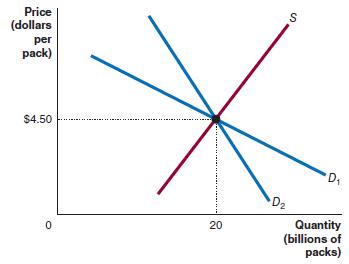
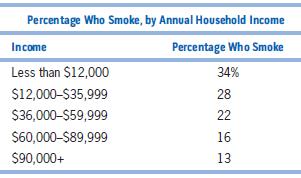
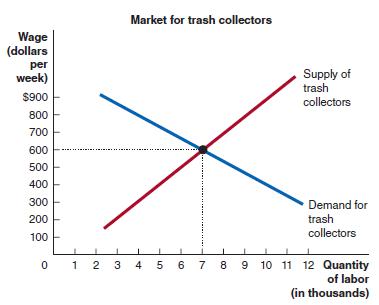
Microeconomics 4th Edition R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien - Solutions
Discover comprehensive resources for "Microeconomics 4th Edition" by R. Glenn Hubbard and Anthony Patrick O’Brien. Access online answers key and solutions manual for all chapters, providing detailed step-by-step answers and solved problems. Enhance your understanding with the test bank and instructor manual, offering a thorough collection of questions and answers. Find solutions in PDF format, perfect for easy reference and study. Whether you're seeking textbook solutions or a free download, our expertly crafted resources deliver clear, concise explanations tailored for your success in mastering microeconomics concepts.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()