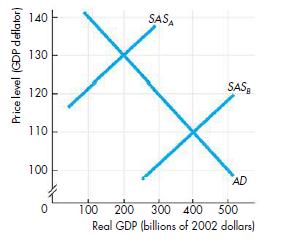
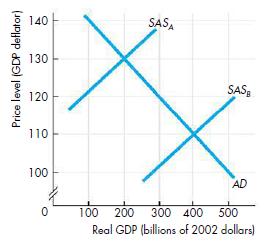
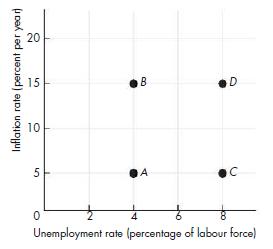
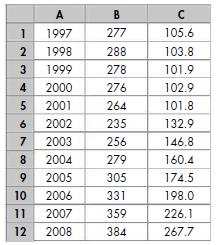
Economics : Canada In The Global Environment 7th Edition King, Harvey B.; Cohen, Avi J. - Solutions
Unlock the complexities of "Economics: Canada In The Global Environment 7th Edition" with our comprehensive solutions. Dive into our online answers key, offering detailed solutions and a complete solution manual in PDF format. Explore solved problems with step-by-step answers, enhancing your understanding of each chapter. Access our extensive test bank and instructor manual to excel in your studies. Our textbook solutions provide a reliable resource for questions and answers, available for free download. Elevate your learning experience with these invaluable resources, designed to offer clarity and insight into economic principles.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()