5. Henry, Tolan, and Gorman-Smith (2001) investigated the effect of ones peers on boys later violence and
Question:
5. Henry, Tolan, and Gorman-Smith (2001) investigated the effect of one’s peers on boys’
later violence and delinquency. Figure 14.21 shows one model drawn from their study,
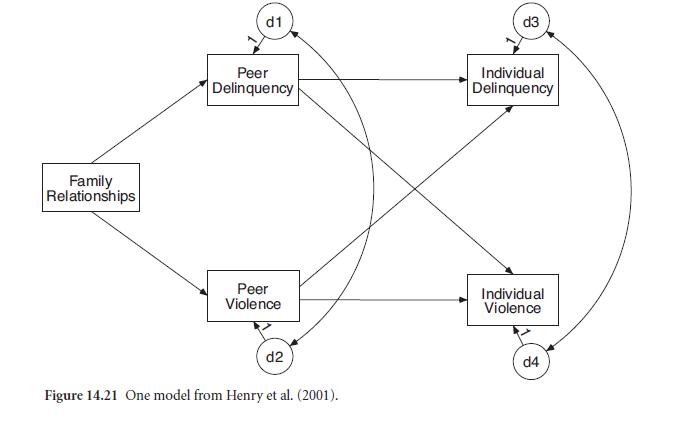
their “fully mediated” model. Family Relationships is a composite of measures of family cohesion, beliefs about family, and family structure, with high scores representing a better functioning family; the violence and delinquency variables are measures of the frequency of violent and nonviolent delinquent offenses for peers and individuals. The model is longitudinal, with Family Relationships measured at age 12, Peer variables at age 14, and Individual variables at age 17. The model is also contained in the file “henry et al.amw” on the Web site.
Data consistent with those reported in the original article are in the SPSS file “Henry et al.sav” or the Excel file “Henry et al.xls.” Analyze and interpret this model. Which variable had a more important effect on boys’ delinquency: peers who are delinquent or peers who are violent? Which variable was more important for boys’ violence? What were the indirect effects of Family Relationships on Individual’s Violence and Delinquency?
Test an alternative model to determine whether Family Relationships directly affect the outcome variables. (The Henry et al., 2001, article reported correlations among variables. The data used in this example were simulated data designed to mimic these correlations. The Family Relationships variable used here was a combination of three variables from the original article.)
Step by Step Answer:







