A large clothing store has recently sent out a special catalogue of fall clothes, and Leiram, its
Question:
A large clothing store has recently sent out a special catalogue of fall clothes, and Leiram, its marketing analyst, wants to find out which customers responded to it and which ones bought the most. She plans to conduct an RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary) analysis. The RFM method is based on the principle that \(80 \%\) of your business comes from the best \(20 \%\) of your customers and states that the following attributes will be useful predictors of who the best customers will be:
- how recently the customer has purchased (Recency)
- how frequently the customer shops (Frequency)
- how much the customer spends (Monetary)
For each customer, Leiram has information for the past five years on Date of Last Purchase, Number of Purchases, and Total Amount Spent. In addition, she has demographic
information, including Age, Marital Status, Sex, Income, and Number of Children. She chooses a random sample of 149 customers who bought something from the catalogue and who have purchased at least three times in the past five years (Number of Purchases). She wants to model how much they bought from the new catalogue (Respond Amount).
Leiram fits the following multiple regression model to the response variable Respond Amount:
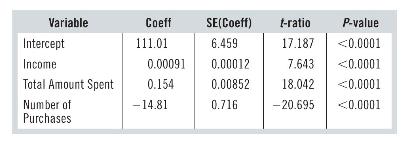
Response Variable: Respond Amount
\(R^{2}=91.48 \%\) Adjusted \(R^{2}=91.31 \%\)
\(S_{e}=18.183\) with \(149-4=145\) degrees of freedom
QUESTIONS:
How much of the variation in Respond Amount is explained by this model? What does the term \(s=18.183\) mean? Which variables seem important in the model?
Step by Step Answer:

Business Statistics
ISBN: 9780136726548
4th Canadian Edition
Authors: Norean Sharpe, Richard De Veaux, Paul Velleman, David Wright





