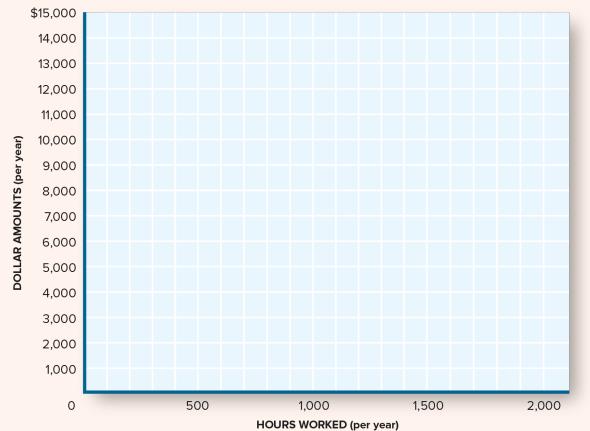
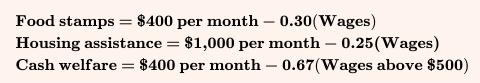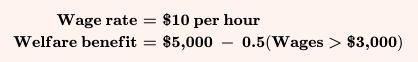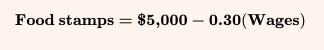The Economy Today 16th Edition Bradley R. Schiller - Solutions
Discover comprehensive solutions for "The Economy Today 16th Edition" by Bradley R. Schiller. Access the online answers key and detailed solutions manual, perfect for students and educators alike. Our platform offers solutions in PDF format, including solved problems and questions and answers from the textbook. Utilize the test bank and chapter solutions for effective study, with step-by-step answers provided for clarity. Instructors can benefit from the instructor manual, enhancing teaching methods. Explore and free download a wealth of resources designed to support your understanding of this essential economic textbook.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()