Question: Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate (iint_{mathcal{S}} mathbf{F} cdot d mathbf{S}) for the given vector field and surface. (mathbf{F}(x, y, z)=leftlangle x y, y z,
Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate \(\iint_{\mathcal{S}} \mathbf{F} \cdot d \mathbf{S}\) for the given vector field and surface.
\(\mathbf{F}(x, y, z)=\left\langle x y, y z, x^{2} z+z^{2}ightangle, \mathcal{S}\) is the boundary of the box \([0,1] \times[2,4] \times[1,5]\).
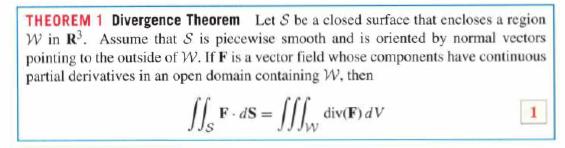
THEOREM 1 Divergence Theorem Let S be a closed surface that encloses a region W in R. Assume that S is piecewise smooth and is oriented by normal vectors pointing to the outside of W. If F is a vector field whose components have continuous partial derivatives in an open domain containing W, then 1 - Sw div(F) dv F-dS=
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The Divergence Theorem relates the flux of a vector field across a closed surface S to the volume in... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


