Nuclear waste is often disposed of by sealing it into containers that are then dumped into the
Question:
Nuclear waste is often disposed of by sealing it into containers that are then dumped into the ocean. It is important to dump the containers into water shallow enough to ensure that they do not break when they hit bottom. Suppose as the container falls through the water, there is a drag force that is proportional to the container’s velocity. Then, it can be shown that the depth s (in meters) of a container of weight W newtons at time t seconds is given by the formula
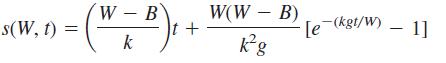
where B is a (constant) buoyancy force, k is the drag constant, and g = 9.8 m/sec2 is the constant acceleration due to gravity.
a. Find ∂s/∂W and ∂s/∂t. Interpret these derivatives as rates. Do you think it is possible for either partial derivative to ever be zero?
b. For a fixed weight, the speed of the container is ∂s/∂t. Suppose the container will break when its speed on impact with the ocean floor exceeds 10 m/sec. If B = 1,983 newtons and k = 0.597 kg/sec, what is the maximum depth for safely dumping a container of weight W = 2,417 newtons?
Step by Step Answer:

Calculus For Business, Economics And The Social And Life Sciences
ISBN: 9780073532387
11th Brief Edition
Authors: Laurence Hoffmann, Gerald Bradley, David Sobecki, Michael Price





