The likelihood that a person with a contagious disease will infect others in a social situation may
Question:
The likelihood that a person with a contagious disease will infect others in a social situation may be assumed to be a function f(s) of the distance s between individuals. Suppose contagious individuals are uniformly distributed throughout a rectangular region R in the xy plane. Then the likelihood of infection for someone at the origin (0, 0) is proportional to the exposure index E, given by the double integral
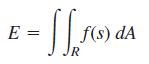
where
![]()
is the distance between (0, 0) and (x, y). Find E for the case where
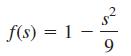
and R is the square R: −2 ≤ x ≤ 2, −2 ≤ y ≤ 2
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Calculus For Business, Economics And The Social And Life Sciences
ISBN: 9780073532387
11th Brief Edition
Authors: Laurence Hoffmann, Gerald Bradley, David Sobecki, Michael Price
Question Posted:





