Question:
Consider the following information about the newly discovered element, vulcium, whose symbol is Vu. ‘Vulcium is a solid at room temperature. It is easily cut by a penknife to reveal a shiny surface which tarnishes quite rapidly. It reacts violently with water, liberating a flammable gas and forms a solution with a pH of 13. When vulcium reacts with chlorine, it forms a white crystalline solid containing 29.5% chlorine.’ (Ar: Vu = 85)
a. Calculate the empirical formula of vulcium chloride.
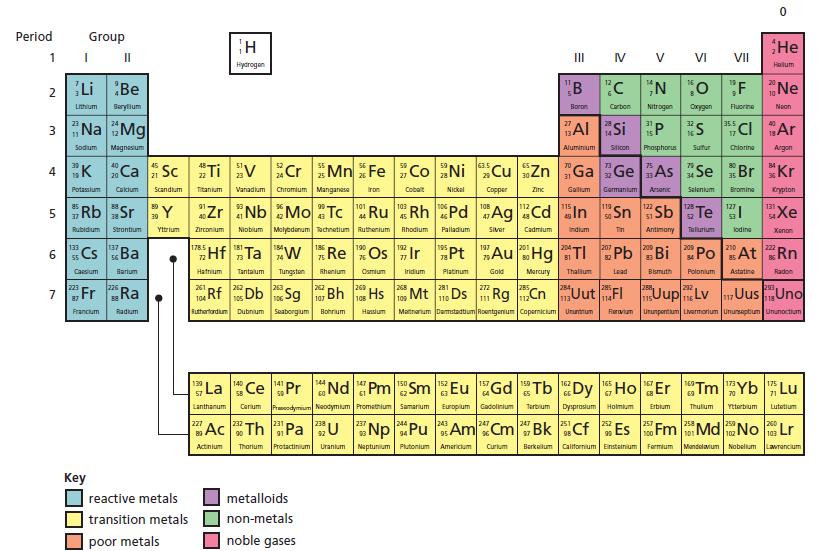
b. To which group of the Periodic Table (p. 136) should vulcium be assigned?
c. Write a word and balanced chemical equation for the reaction between vulcium and chlorine.
d. What other information in the description supports the assignment of group you have given to vulcium?
e. What type of bonding is present in vulcium chloride?
f. Write a word and balanced chemical equation for the reaction between vulcium and water.
g. Write the formulae for:
(i) Vulcium sulfate
(ii) Vulcium carbonate
(iii) Vulcium hydroxide.
Look at the Periodic Table to find out the real name of vulcium.
Periodic Table
Transcribed Image Text:
Period Group Не 1 I I| III V v VI II Hydrogen Halum "B CN o F Ne 20 2 Li Be 10 Lithium Barylium Boron Carbon Nitrogen Onygen Fluorine Noon 3 Na Mg Al Si P S CI Ar LE 15 22 28 32 35.5 17 Sodum Magnasium Argon Aluminium Siicon Phosphorus Sutur Chiorina 4 K Ca ScTi V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn"Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 63.5 75 79 80 Vanadium Chromium Manganesa Germantum Potassium Calium Scandtum Titanium Iron Cobalt Nickal Copper Zinc Galium Arsanic Salanium Bromine Krypton Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te 112 119 5Rb Sr Y 91 T06 115 122 128 127 Xe 131 Rubidium Strontium Ytrium Zirconium Niobium Molyedanum Tachnetium Rutherium Ahodium Palladium Siver Cadmium Indium Tin Antimony Rallurium lodine Kenon Hf Ta w ERe 0s Pt AUH9 TPb 181 190 201 207 200 222 133 137 178.5 186 192 195 197 Bi 209 Po At Rn 210 Cs Ba 56 72 Tungsten Astatine Caesium Barium Hatnium Tantalum Rhenium Osmium Iridium Platinum Gold Marcury Thalium Laad Bismuth Polonium Radon 263 Fr Ra z26 262 269 268 285 223 7 284, 113 261 262 281 272 28 288 292 Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Cn Uut FI UupLv UusUno B7 106 117 118 Buthartordium Matnanum Damstadtium Roentganium Coparnicium Ununtnum Ununpentum Livermorium ununaptium Ununoctium Francum Radum Dubnium Seaborgium Bohrium Hassium Fervum La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy HoEr Tm Yb Lu 140 144 150 152 157 165 167 57 Lanthanum Praneodymium Neodymium Promathium Samarum Europium Cadolinium Tarbium Dysproslum Holmlum Erbium Thullum Ytterbium Lutetium 258 Ac Th Pa U Np Pu AmCm Bk Cf Es Fm MdNo Lr 227 231 244 243 247 251 259 260 232 238 237 252 257 100 1102 Tharium Protactinium Uranium Neptunium| Plutonium Barkelum Calitornium Einstainium Fermium Mandolavium Nobelum LaWTencium Actinium Americium Curlum Key reactive metals metalloids transition metals non-metals poor metals noble gases







