It is possible that hydrogen and other gases dissociate when adsorbed on a solid surface, and in
Question:
It is possible that hydrogen and other gases dissociate when adsorbed on a solid surface, and in catalysis it is important to know whether such a dissociation occurs. If hydrogen did not dissociate, that is, the adsorption process was
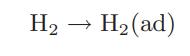
the amount of hydrogen adsorbed would be given by Amount of H2 adsorbed = K1aH2 where aH2 is the activity of molecular hydrogen in the gas phase. However, if hydrogen dissociates, the following two-step process occurs at the surface:

Using the notation that K2 is the activity-based equilibrium constant for the dissociation reaction, develop expressions for the amount of molecular hydrogen adsorbed as a function of the equilibrium constants and the hydrogen partial pressure for the two cases (adsorption without dissociation and adsorption with dissociation). How would you discern which process was occurring if you had experimental data on the total hydrogen adsorption as a function of its partial pressure?
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Biochemical And Engineering Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9780470504796
5th Edition
Authors: Stanley I. Sandler