Question: Redo Problem 4.18 using Aspen Plus. Problem 4.18 If it is necessary to compress hydrogen to a higher pressure than is possible with the single-compression
Redo Problem 4.18 using Aspen Plus.
Problem 4.18
If it is necessary to compress hydrogen to a higher pressure than is possible with the single-compression step above, an alternative is to use two compressors (or a two-stage compressor) with intercooling. In such a process the hydrogen is compressed in the first stage of the compressor, then cooled at constant pressure to a lower temperature, and then compressed further in a second compressor or stage. Although it may not be economical to do so, more than two stages can be used.
a. Compute the maximum pressure that can be obtained in a two-stage compression with intercooling to 300 K between the stages, assuming hydrogen to be an ideal gas with the heat capacity given in Appendix A.II.
b. Repeat the calculation above for a three-stage compression with intercooling to 300 K.
Appendix A.II
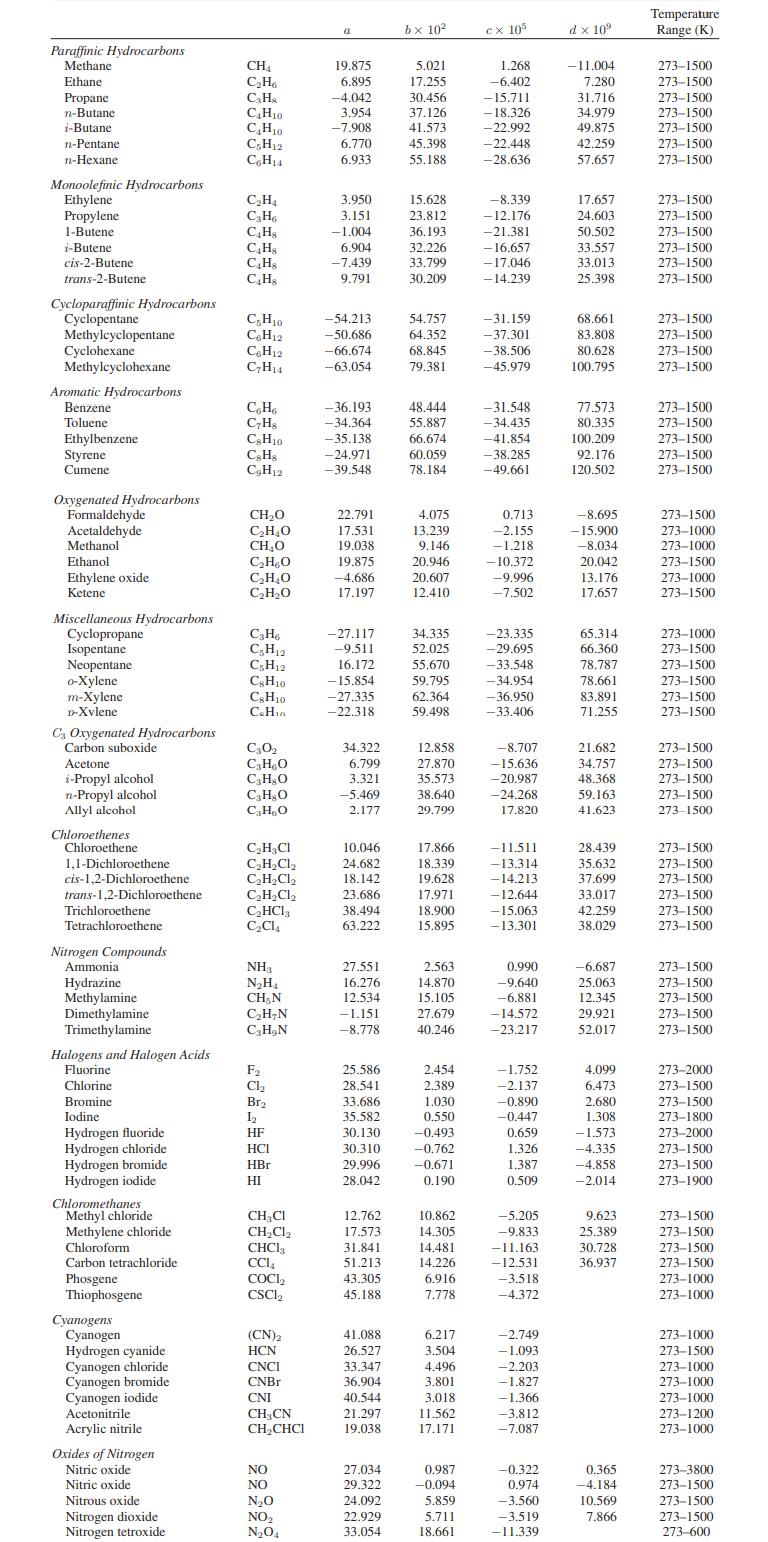
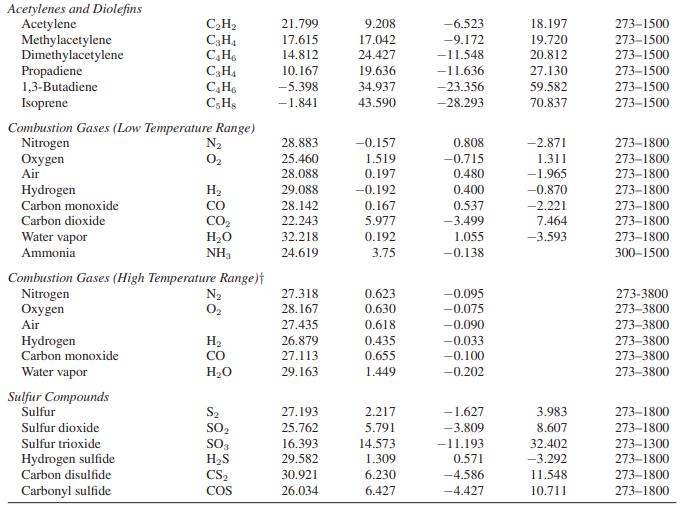
Paraffinic Hydrocarbons Methane Ethane Propane n-Butane i-Butane n-Pentane n-Hexane Monoolefinic Hydrocarbons Ethylene Propylene 1-Butene i-Butene cis-2-Butene trans-2-Butene Cycloparaffinic Hydrocarbons Cyclopentane Methylcyclopentane Cyclohexane Methylcyclohexane Aromatic Hydrocarbons Benzene Toluene Ethylbenzene Styrene Cumene Oxygenated Hydrocarbons Formaldehyde Acetaldehyde Methanol Ethanol Ethylene oxide Ketene Miscellaneous Hydrocarbons Cyclopropane Isopentane Neopentane o-Xylene m-Xylene D-Xvlene C3 Oxygenated Hydrocarbons Carbon suboxide Acetone i-Propyl alcohol n-Propyl alcohol Allyl alcohol Chloroethenes Chloroethene 1,1-Dichloroethene cis-1,2-Dichloroethene trans-1,2-Dichloroethene Trichloroethene Tetrachloroethene. Nitrogen Compounds Ammonial Hydrazine Methylamine Dimethylamine Trimethylamine Halogens and Halogen Acids Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine Hydrogen fluoride Hydrogen chloride Hydrogen bromide Hydrogen iodide Chloromethanes Methyl chloride Methylene chloride Chloroform Carbon tetrachloride Phosgene Thiophosgene Cyanogens Cyanogen Hydrogen cyanide Cyanogen chloride Cyanogen bromide Cyanogen iodide Acetonitrile Acrylic nitrile Oxides of Nitrogen Nitric oxide Nitric oxide Nitrous oxide Nitrogen dioxide Nitrogen tetroxide CH CH6 CH C4H10 CH0 C5H12 C6H14 CH CH6 C4H8 C4H8 C4Hs C4H8 C5H10 C6H12 C6H12 CH14 C6H6 CH8 CH10 CsH8 CH12 CHO CHO CHO CHBO CHO CHO C3H6 CH12 C5H12 CH10 C&H10 C.Hin C30 C3HO C3H8O CHO CHO CHCl CHCl CHCl CHCl CHCl3 CC14 NH3 NH CH, N CHN CHN F Cl Br 1 HF HCI HBr HI CHCl CHCl CHC13 CC14 COCI CSCL (CN)2 HCN CNCI CNBr CNI CH3CN CHCHCI NO NO NO NO NO4 a 19.875 6.895 -4.042 3.954 -7.908 6.770 6.933 3.950 3.151 -1.004 6.904 -7.439 9.791 -54.213 -50.686 -66.674 -63.054 -36.193 -34.364 -35.138 -24.971 -39.548 22.791 17.531 19.038 19.875 -4.686 17.197 -27.117 -9.511 16.172 -15.854 -27.335 -22.318 34.322 6.799 3.321 -5.469 2.177 10.046 24.682 18.142 23.686 38.494 63.222 27.551 16.276 12.534 -1.151 -8.778 25.586 28.541 33.686 35.582 30.130 30.310 29.996 28.042 12.762 17.573 31.841 51.213 43.305 45.188 41.088 26.527 33.347 36.904 40.544 21.297 19.038 27.034 29.322 24.092 22.929 33.054 bx 10 5.021 17.255 30.456 37.126 41.573 45.398 55.188 15.628 23.812 36.193 32.226 33.799 30.209 54.757 64.352 68.845 79.381 48.444 55.887 66.674 60.059 78.184 4.075 13.239 9.146 20.946 20.607 12.410 34.335 52.025 55.670 59.795 62.364 59.498 12.858 27.870 35.573 38.640 29.799 17.866 18.339 19.628 17.971 18.900 15.895 2.563 14.870 15.105 27.679 40.246 2.454 2.389 1.030 0.550 -0.493 -0.762 -0.671 0.190 10.862 14.305 14.481 14.226 6.916 7.778 6.217 3.504 4.496 3.801 3,018 11.562 17.171 0.987 -0.094 5.859 5.711 18.661 cx 105 1.268 -6.402 -15.711 -18.326 -22.992 -22.448 -28.636 -8.339 -12.176 -21.381 -16.657 -17.046 -14.239 -31.159 -37.301 -38.506 -45.979 -31.548 -34.435 -41.854 -38.285 -49.661 0.713 -2.155 -1.218 -10.372 -9.996 -7.502 -23.335 -29.695 -33.548 -34.954 -36.950 -33.406 -8.707 -15.636 -20.987 -24.268 17.820 -11.511 -13.314 -14.213 -12.644 -15.063 -13.301 0.990 -9.640 -6.881 -14.572 -23.217 -1.752 -2.137 -0.890 -0.447 0.659 1.326 1.387 0.509 -5.205 -9.833 -11.163 -12.531 -3.518 -4.372 -2.749 -1.093 -2.203 -1.827 -1.366 -3.812 -7.087 -0.322 0.974 -3.560 -3.519 -11.339 d x 10 -11.004 7.280 31.716 34.979 49.875 42.259 57.657 17.657 24.603 50.502 33.557 33.013 25.398 68.661 83.808 80.628 100.795 77.573 80.335 100.209 92.176 120.502 -8.695 -15.900 -8.034 20.042 13.176 17.657 65.314 66.360 78.787 78.661 83.891 71.255 21.682 34.757 48.368 59.163 41.623 28.439 35.632 37.699 33.017 42.259 38.029 -6.687 25.063 12.345 29.921 52.017 4.099 6.473 2.680 1.308 -1.573 -4.335 -4.858 -2.014 9.623 25.389 30.728 36.937 0.365 -4.184 10.569 7.866 Temperature Range (K) 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1000 273-1000 273-1500 273-1000 273-1500 273-1000 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-2000 273-1500 273-1500 273-1800 273-2000 273-1500 273-1500 273-1900 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-1000 273-1000 273-1000 273-1500 273-1000 273-1000 273-1000 273-1200 273-1000 273-3800 273-1500 273-1500 273-1500 273-600
Step by Step Solution
3.35 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


