A column arrangement similar to Figure (15-2) is used for organic liquids. A large reservoir of water
Question:
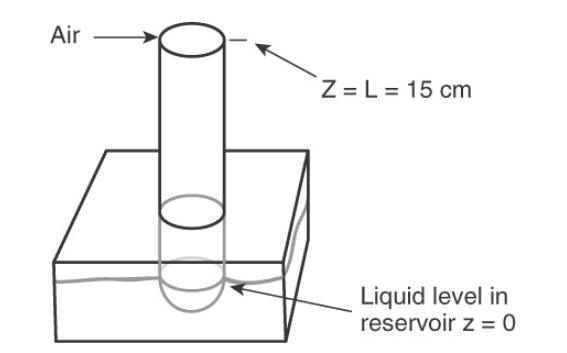
A column arrangement similar to Figure \(15-2\) is used for organic liquids. A large reservoir of water is under the column. The water is stirred and solute concentration in the water is constant. The organic liquid is immiscible in water and floats on the water surface at \(\mathrm{z}=0\). Mole fractions \(\mathrm{x}\) of the two layers in equilibrium are related by \(\mathrm{K}=\) \(\mathrm{x}_{\text {solute,organic }} / \mathrm{x}_{\text {solute,water }}\). At \(\mathrm{z}=\mathrm{L}=20 \mathrm{~cm}\) (top of the column) mole fraction of solute in the organic liquid is zero. The entire apparatus is at \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and 1.0 bar. The column cross-sectional area is \(0.55 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}\). Diffusion of solute, benzoic acid \(\left(\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{COOH}\right)\), in toluene \(\left(\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{5} \mathrm{CH}_{3}\right)\) is studied. Assume toluene is totally immiscible in water. The mole fraction of benzoic acid in the water is kept constant at \(=0.00212\) mole fraction. Calculate benzoic acid flux in \(\mathrm{mol} /\left(\mathrm{m}^{2} \mathrm{~s}\right)\).
Data: Diffusion coefficient of benzoic acid in toluene at \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}=1.5 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}^{2} / \mathrm{s}\). MW toluene \(=92.14 \mathrm{~g} / \mathrm{mol}\), MW water \(=18 \mathrm{~g} / \mathrm{mol}\), MW benzoic acid \(=122.12 \mathrm{~g} / \mathrm{mol}\). Density toluene \(=865 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\), density water \(=1000 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\).
\(\mathrm{K}\left(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right)=123.1=\mathrm{x}_{\text {benzoic_acid_in_toluene }} / \mathrm{x}_{\text {benzoic_acid_in_water }}\)
Figure (15-22)
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





