A thermocouple well, sketched in Fig. P.4.7, is used to measure the temperature of the air flowing
Question:
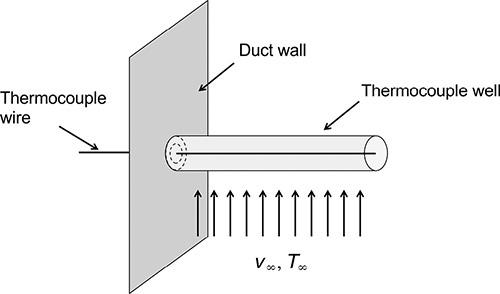
A thermocouple well, sketched in Fig. P.4.7, is used to measure the temperature of the air flowing inside a metal duct at a velocity of 10 m/s.
The well consists of a cylindrical copper tube (0.01 m outside diameter, 0.001 m wall thickness, and 0.1 m long) which is closed at the end that protrudes into the flowing gas stream and is soldered to the duct wall at the other end. A thin thermocouple wire is placed in the well and senses the temperature at its closed end. The duct wall temperature is 300 K, and the temperature indicated by the thermocouple is 313 K. The heat transfer coefficient describing convective heat transfer from the air to the thermocouple well is estimated to be h = 50 W/m2 K. Assuming steady state, determine the actual temperature of the flowing air. Note that heat conduction from the duct wall will affect the temperature reading. Suggest ways in which we can make the thermocouple readout closer to the actual stream temperature.
FIGURE P.4.7:
Step by Step Answer:

Heat And Mass Transfer For Chemical Engineers Principles And Applications
ISBN: 9781264266678
1st Edition
Authors: Giorgio Carta





