Nitromethane and water are separated in a rectifying column system with a total condenser and a liquid-liquid
Question:
Nitromethane and water are separated in a rectifying column system with a total condenser and a liquid-liquid settler similar to Figure 8-3A, except the column is a rectifying column. The saturated vapor feed is \(7.5 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) water. The water product from the settler is \(91.4 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) water. The organic phase refluxed to the column is \(31.2 \mathrm{~mol} \%\) water. Pressure \(=1.0 \mathrm{~atm}\), feed rate \(=50.0 \mathrm{kmol} / \mathrm{h}\), and \(\mathrm{CMO}\) is valid. The desired bottoms is 2.5 \(\mathrm{mol} \%\) water.
Figure 8-3A
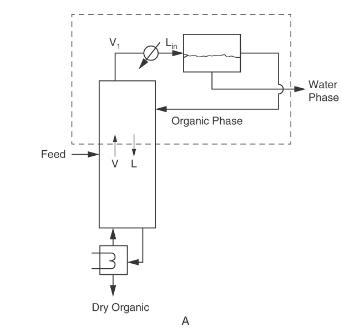
Find: \(\mathrm{x}_{\text {dist,water }}\), reflux ratio \(\mathrm{L} / \mathrm{D}, \mathrm{D}, \mathrm{B}\), and the number of equilibrium stages.
Equilibrium data are in Table 8-8. Density data are given after the table, and be sure to read the note on safety at the end of this problem.
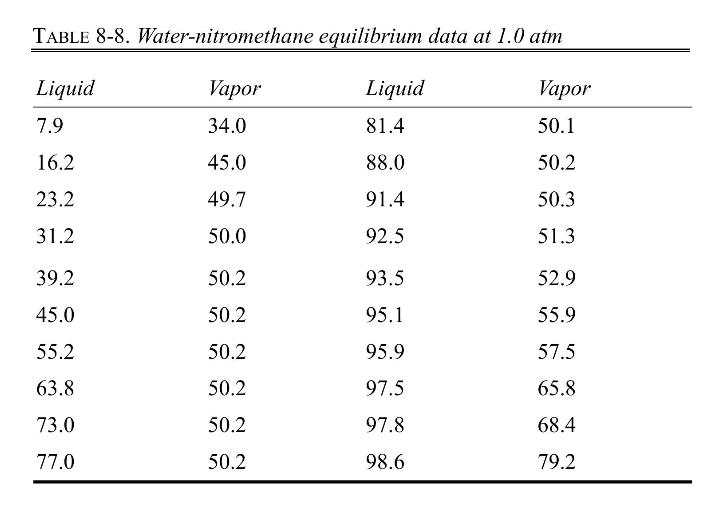
Data: Density of nitromethane at \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) is \(1129 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\).
Safety note: Nitromethane (also called methyl nitrate, \(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{NO}_{2}\) ) is dangerous. If you try to freeze the pure compound, it explodes.
Step by Step Answer:

Separation Process Engineering Includes Mass Transfer Analysis
ISBN: 9780137468041
5th Edition
Authors: Phillip Wankat





