Question: Two solutions are separated by a porous sintered disk ( (1 mathrm{~mm}) thick) that permits diffusion across the disk. On one side we have a
Two solutions are separated by a porous sintered disk ( \(1 \mathrm{~mm}\) thick) that permits diffusion across the disk. On one side we have a mixture of \(1 \mathrm{M} \mathrm{HCl}\) and \(1 \mathrm{M} \mathrm{BaCl}_{2}\) while on the other side we have pure water. It is required to find the flux across the system. Both salts are completely ionized and diffuse as \(\mathrm{H}^{+}, \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\), and \(\mathrm{Ba}^{2+}\) across the disk. Set up the model to compute the fluxes. From the fluxes, find the effective diffusivities of these ions across the disk.
Use for the ionic diffusivity for Ba ions \(0.85 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{~m}^{2} / \mathrm{s}\). For the other ions, use the values in Table 22.1.
Use the condition of no net current to solve for the potential.
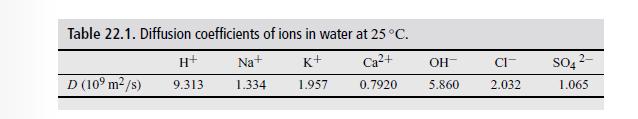
Table 22.1. Diffusion coefficients of ions in water at 25 C. H+ Na+ K+ Ca+ OH- CI- D (109 m/s) SO42- 9.313 1.334 1.957 0.7920 5.860 2.032 1.065
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


