Question: Consider the cooler, (mathrm{H} 2), in the monochlorobenzene separation process in Figures 7.21 and 7.22. Assume that the heat is transferred to an infinite reservoir
Consider the cooler, \(\mathrm{H} 2\), in the monochlorobenzene separation process in Figures 7.21 and 7.22. Assume that the heat is transferred to an infinite reservoir of cooling water at \(77^{\circ} \mathrm{F}\).
(a) Using the enthalpy and entropy values in the results for the sample problem in the ASPEN PLUS section of the multimedia modules that can be downloaded from www.seas.upenn.edu/ dlewin/multimedia.html, determine the lost work associated with the cooler.
(b) Let the reservoir be at \(100^{\circ} \mathrm{F}\) and repeat (a).
Figure 7.21:-
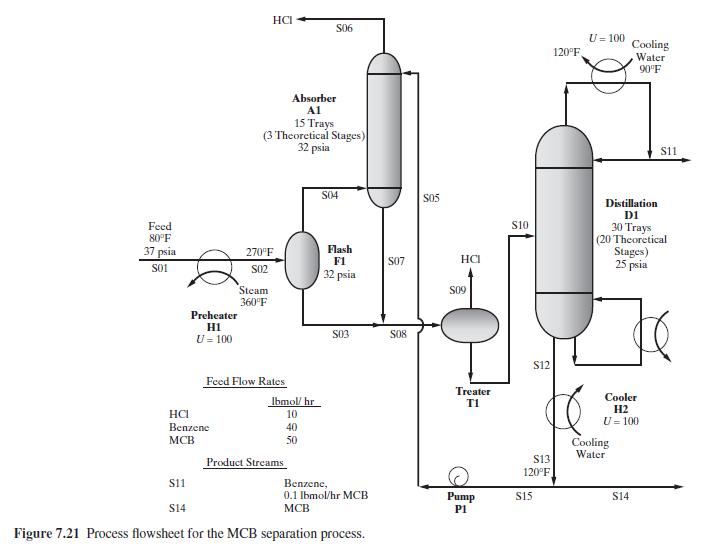
Figure 7.22:-
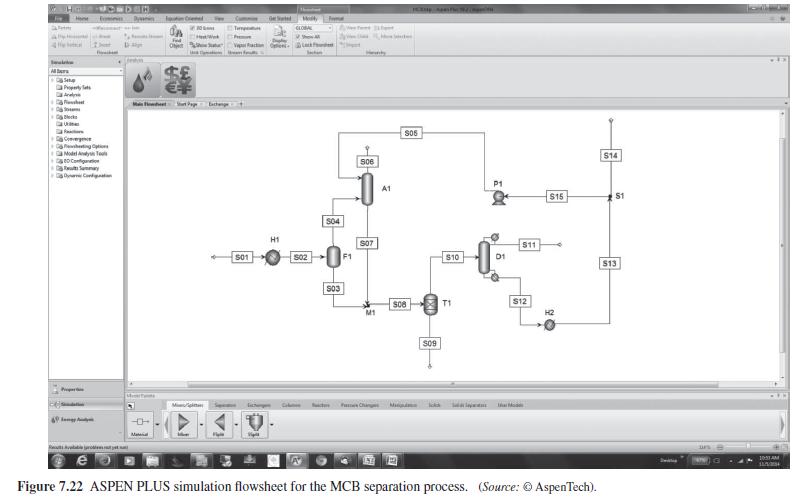
Feed HCI S06 Absorber A1 15 Trays (3 Theoretical Stages) 32 psia S04 S05 S10 80F 37 psia 270F Flash F1 S07 HCI S01 S02 32 psia Steam S09 360F Preheater H1 S03 S08 U=100 Feed Flow Rates S12 lbmol/ hr Treater T1 HCI 10 Benzene 40 MCB 50 Product Streams $13 120F S11 Benzene, 0.1 lbmol/hr MCB $14 MCB Pump P1 $15 Figure 7.21 Process flowsheet for the MCB separation process. 120F U=100 Cooling Water 90F $11 Distillation D1 30 Trays (20 Theoretical Stages) 25 psia Cooler H2 U=100 Cooling Water S14
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (161 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


