Consider an apparatus in which A and B are two 1.00-L flasks joined by a stopcock C.
Question:
Consider an apparatus in which A and B are two 1.00-L flasks joined by a stopcock C. The volume of the stopcock is negligible. Initially, A and B are evacuated, the stopcock C is closed, and 1.50 g of diethyl ether, C2H5OC2H5, is introduced into flask A. The vapor pressure of diethyl ether is 57 Torr at –45°C, 185 Torr at 0°C, 534 Torr at 25°C, and negligible below –86°C.
(a) If the stopcock is left closed and the flask is brought to equilibrium at –45°C, what will be the pressure of diethyl ether in flask A?
(b) If the temperature is raised to 25°C, what will be the pressure of diethyl ether in the flask?
(c) If the temperature of the assembly is returned to –45°C and the stopcock C is opened, what will be the pressure of diethyl ether in the apparatus?
(d) If flask A is maintained at –45 °C and flask B is cooled with liquid nitrogen (boiling point, –196 °C) with the stopcock open, what changes will take place in the apparatus? Assume ideal behavior.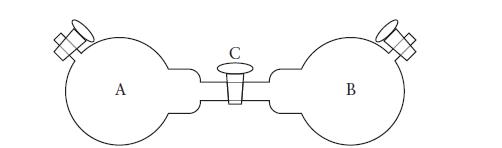
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight
ISBN: 9781464183959
7th Edition
Authors: Peter Atkins, Loretta Jones, Leroy Laverman





