Question:
If you were an analytical chemist, one test you might use for the presence of iron(III) ions is to add a solution of potassium thiocyanate, KSCN; a blood-red color indicates that a compound of iron and the thiocyanate ion has formed. Write three Lewis structures with different atomic arrangements for the thiocyanate ion and select the most likely structure by identifying the structure with formal charges closest to zero. For simplicity, consider only structures with double bonds between neighboring atoms.
ANTICIPATE The element with the lowest ionization energy (after you have read Topic 2D, you will find it is more appropriate to think “lowest electronegativity”) of the three is carbon, so you should expect it to be the central atom and for the structure to be NCS 2 .
PLAN Proceed as set out in Toolbox 2B.2.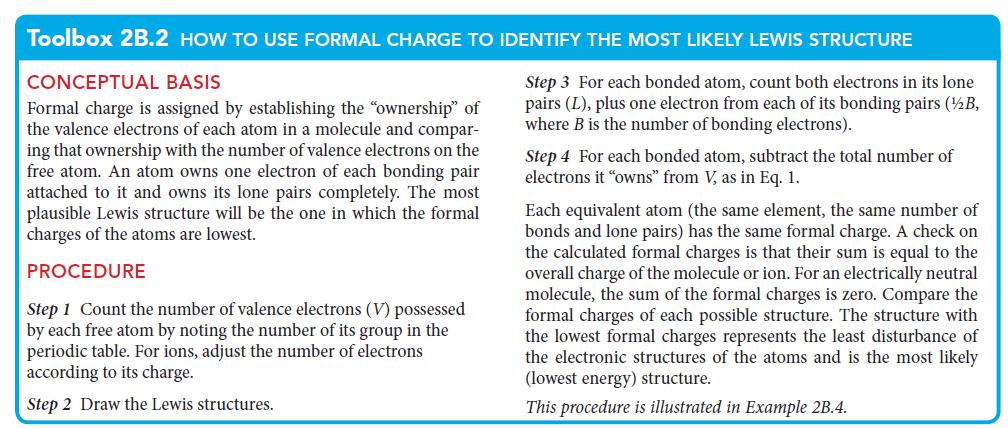
Transcribed Image Text:
Toolbox 2B.2 HOW TO USE FORMAL CHARGE TO IDENTIFY THE MOST LIKELY LEWIS STRUCTURE
CONCEPTUAL BASIS
Step 3 For each bonded atom, count both electrons in its lone
pairs (L), plus one electron from each of its bonding pairs (½/B,
where B is the number of bonding electrons).
Formal charge is assigned by establishing the "ownership" of
the valence electrons of each atom in a molecule and compar-
ing that ownership with the number of valence electrons on the
free atom. An atom owns one electron of each bonding pair
attached to it and owns its lone pairs completely. The most
plausible Lewis structure will be the one in which the formal
charges of the atoms are lowest.
PROCEDURE
Step 1 Count the number of valence electrons (V) possessed
by each free atom by noting the number of its group in the
periodic table. For ions, adjust the number of electrons
according to its charge.
Step 2 Draw the Lewis structures.
Step 4 For each bonded atom, subtract the total number of
electrons it "owns" from V, as in Eq. 1.
Each equivalent atom (the same element, the same number of
bonds and lone pairs) has the same formal charge. A check on
the calculated formal charges is that their sum is equal to the
overall charge of the molecule or ion. For an electrically neutral
molecule, the sum of the formal charges is zero. Compare the
formal charges of each possible structure. The structure with
the lowest formal charges represents the least disturbance of
the electronic structures of the atoms and is the most likely
(lowest energy) structure.
This procedure is illustrated in Example 2B.4.







