Sometimes scientists are surprised by apparently anomalous properties of the materials they study. When those anomalies are
Question:
Sometimes scientists are surprised by apparently anomalous properties of the materials they study. When those anomalies are considered, they can reveal information about the structure of matter. Calculate the entropy of a tiny solid made up of four diatomic molecules of a compound such as carbon monoxide, CO, at T = 0 when
(a) The four molecules have formed a perfectly ordered crystal in which all molecules are aligned with their C atoms on the left (top left image in FIG. 4G.2) and
(b) The four molecules lie in random orientations (but parallel, as in any of the images in Fig. 4G.2).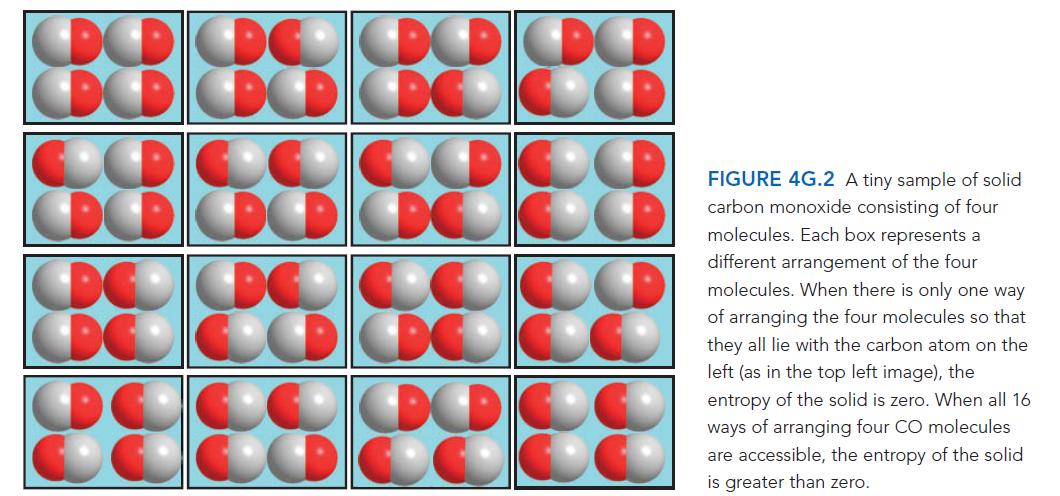
ANTICIPATE You should expect that at T = 0 the sample in
(a) Will have zero entropy, because there is no disorder in either location or energy—all the molecules are in their lowest possible energy state. The sample in
(b) Has greater disorder, so you should expect its entropy to be greater than 0.
PLAN To find the number of microstates for a system, first determine the number of orientations, O, that each molecule can adopt and that have the same energy. Since each molecule can adopt O orientations, the number of microstates is O taken N times, O * O * O…, where N is the total number of molecules in the system. The number of microstates in a system of this kind is therefore W = ON. Then use that value of W in the Boltzmann formula (Eq. 1) to calculate the entropy of the sample.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight
ISBN: 9781464183959
7th Edition
Authors: Peter Atkins, Loretta Jones, Leroy Laverman





