The nitrogen oxides are common pollutants generated by internal combustion engines and power plants. They not only
Question:
The nitrogen oxides are common pollutants generated by internal combustion engines and power plants. They not only contribute to the respiratory distress caused by smog but, if they reach the stratosphere, they also threaten the ozone layer that protects Earth from harmful radiation.
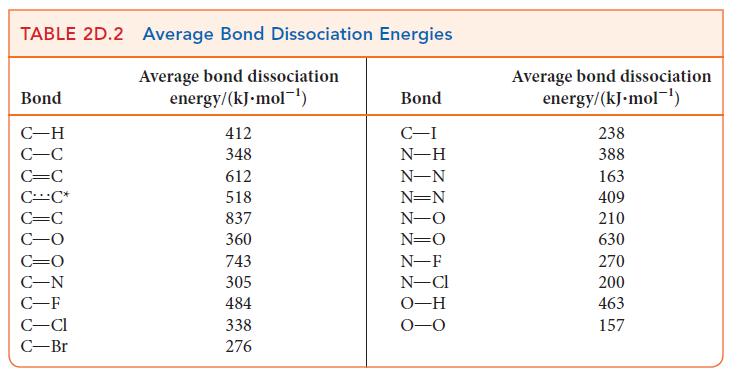
(a) The bond energy in NO is 632 kJ · mol–1 and that of each N—O bond in NO2 is 469 kJ · mol–1. Use Lewis structures and the average bond energies in Table 2D.2 to explain the difference in bond energies between the two molecules and the fact that the bond energies of the two bonds in NO2 are the same.
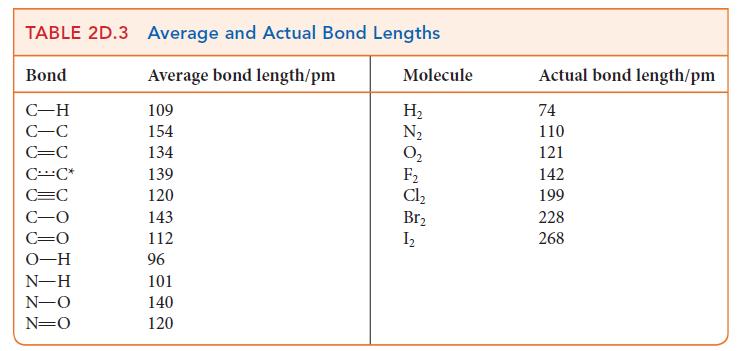
(b) The bond length in NO is 115 pm. Use Fig. 2D.11 to predict the length of a single bond and a double bond between nitrogen and oxygen. Use Table 2D.3 to estimate the length of a triple bond between nitrogen and oxygen. Predict the bond order in NO from its bond length and explain any difference from the calculated values.
(c) When the NO in smog reacts with NO2, a bond forms between the two N atoms. Draw the Lewis structure of each reactant and the product and indicate the formal charge on each atom.
(d) The NO2 in smog also reacts with NO3 to form a product with an O atom between the two N atoms. Draw the Lewis structure of the most likely product and indicate the formal charge on each atom.
(e) Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of the product from part (d) with water to produce an acid. The acid produced acts as a secondary pollutant in the environment. Name the acid.
(f) If 4.05 g of the product from part (d) reacts with water as in part (e) to produce 1.00 L of acidic solution, what will be the molar concentration of the acid?
(g) Determine the oxidation number of nitrogen in NO, NO2, and the products in parts (c) and (d). Which of these compounds would you expect to be the most potent oxidizing agent?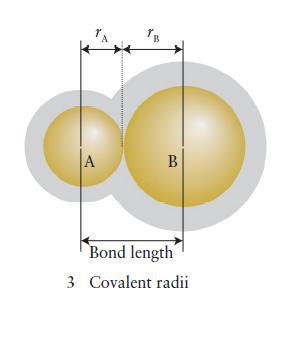
Step by Step Answer:

Chemical Principles The Quest For Insight
ISBN: 9781464183959
7th Edition
Authors: Peter Atkins, Loretta Jones, Leroy Laverman





