Question: The elementary isomerization reaction A B is taking place on the walls of a cylindrical catalyst pore (see Figure P15-7B.) In one run, a
The elementary isomerization reaction A → B is taking place on the walls of a cylindrical catalyst pore (see Figure P15-7B.) In one run, a catalyst poison P entered the reactor together with the reactant A. To estimate the effect of poisoning, we assume that the poison renders the catalyst pore walls near the pore mouth ineffective up to a distance z1, so that no reaction takes place on the walls in this entry region.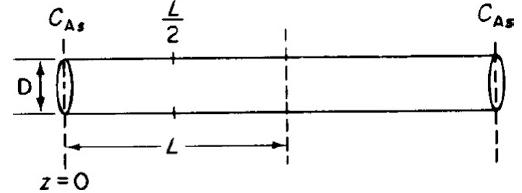 a. Show that before poisoning of the pore occurred, the effectiveness factor was given by
a. Show that before poisoning of the pore occurred, the effectiveness factor was given by
η=1ϕ tanh ϕ
where
ϕ=L2krDe
with
k=reaction-rate constant (lenght/time)r=pore radius (length)De=effective molecular diffusivity (area/time)
b. Derive an expression for the concentration profile and also for the molar flux of A in the ineffective region, 0 1, in terms of z1, DAB, CA1, and CAs. Without solving any further differential equations, obtain the new effectiveness factor η′ for the poisoned pore.
CAS z=0 2 7 CAS
Step by Step Solution
3.24 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a b Given A B on the walls of a cylindrical catalyst pore Z length of poisone... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


