The steering rockets in space vehicles use N 2 O 4 and a derivative of hydrazine, 1,1-dimethylhydrazine
Question:
The steering rockets in space vehicles use N2O4 and a derivative of hydrazine, 1,1-dimethylhydrazine (Study Question 5.86). This mixture is called a hypergolic fuel because it ignites when the reactants come into contact:![]()
(a) Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent in this reaction.
(b) The same propulsion system was used by the Lunar Lander on moon missions in the 1970s. If the Lander used 4100 kg of H2NN(CH3)2, what mass (in kilograms) of N2O4 was required to react with it? What mass (in kilograms) of each of the reaction products was generated?
Data given in Question 86
Hydrazine and 1,1-dimethylhydrazine both react spontaneously with O2 and can be used as rocket fuels.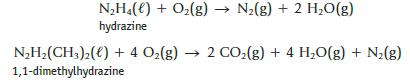
The molar enthalpy of formation of N2H4(ℓ) is +50.6 kJ/mol, and that of N2H2(CH3)2(ℓ) is +48.9 kJ/mol. Use these values, with other Δf H° values, to decide whether the reaction of hydrazine or 1,1-dimethylhydrazine with oxygen provides more energy per gram.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry And Chemical Reactivity
ISBN: 9780357001172
10th Edition
Authors: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel





