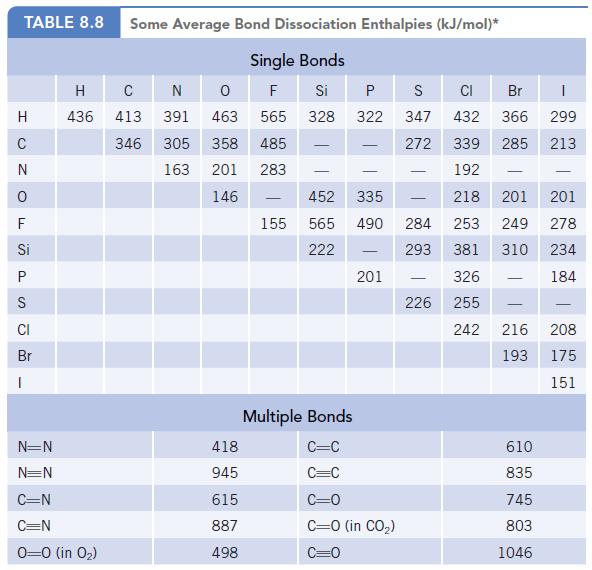
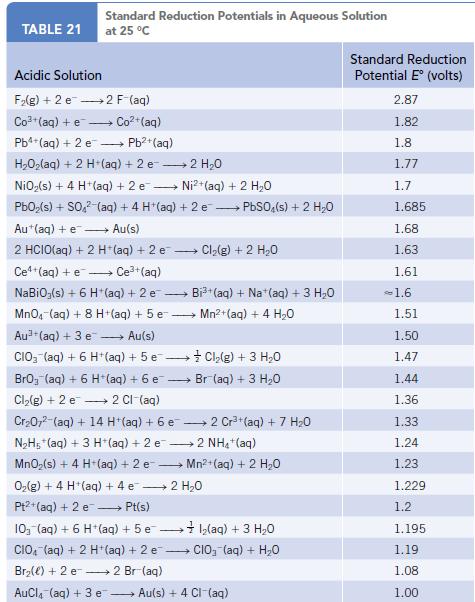
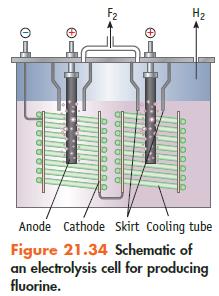
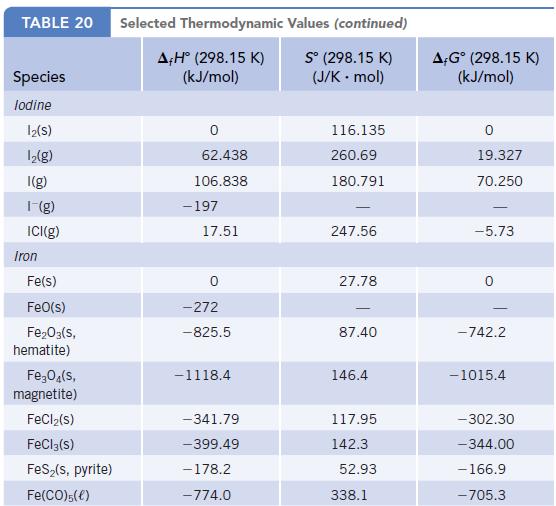
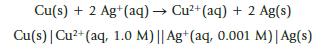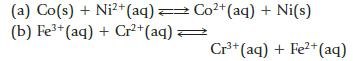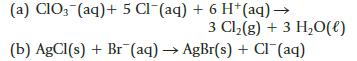Chemistry And Chemical Reactivity 10th Edition John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel - Solutions
Discover comprehensive resources for "Chemistry And Chemical Reactivity 10th Edition" by John C. Kotz and others, including an extensive online answers key. Access the solution manual and solutions PDF to find expertly solved problems and clear step-by-step answers. Enhance your understanding with questions and answers from the test bank, and delve into detailed chapter solutions. Whether you're a student or an instructor, the textbook and instructor manual provide invaluable insights. Enjoy the convenience of a free download to support your studies and maximize your learning experience with this essential guide.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


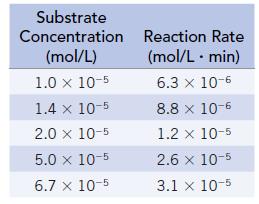
![[S], mol/L 2.500 1.00 0.714 0.526 0.250 Rate, mmol/min 0.588 0.500 0.417 0.370 0.256](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1698/2/2/0/9286538cb805e6d31698220928501.jpg)