A chemist uses the apparatus shown in Figure 3.4 to determine the composition of a compound made
Question:
A chemist uses the apparatus shown in Figure 3.4 to determine the composition of a compound made up of only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. During combustion of a 0.1000-g sample , the mass of the first trap (collecting H2O) increased by 0.0928 g H2O and the mass of the second trap (collecting CO2) increased by 0.228 g CO2. (Note that it is possible for the sum of the masses of the H2O and CO2 to be greater than the mass of the starting sample because some of the oxygen in the products comes from the added O2.) Calculate the mass and mass percentage of each element in the 0.1000-g sample.
Figure 3.4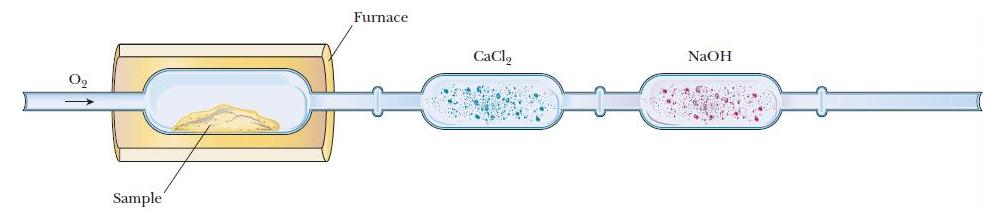
Strategy
The formulas of water and carbon dioxide, coupled with the periodic table, allow the conversion of mass of each compound to mass of the two respective elements by using the following sequence: mass compound → moles compound; moles compound → moles of element; moles element → grams element. Oxygen is calculated by difference from the mass of C and H, and the total mass of the sample.
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry Principles And Practice
ISBN: 9780534420123
3rd Edition
Authors: Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball





